KY الدجاجة
| KY Cygni | |
|---|---|
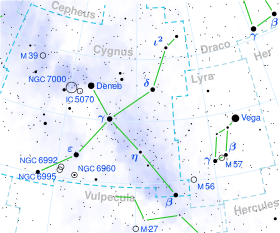
موقع النجم في كوكبة الدجاجة
| |
| معلومات الرصد حقبة حقبة (فلك) اعتدالان حقبة (فلك) |
|
| كوكبة | الدجاجة (كوكبة) |
| مطلع مستقيم | 20سا 25د 58.05ث[1] |
| الميل | +38° 21′ 07.6″[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 11.14[2] (10.60 - 11.74[3]) |
| الخصائص | |
| مرحلة التطور | M3-4I[4] (M3.5Ia[5]) |
| مرحلة التطور | M3-4I[4] (M3.5Ia[5]) |
| U−B مؤشر اللون | +2.91[2] |
| B−V مؤشر اللون | +3.39[2] |
| نوع التغير | LC[5] |
| القياسات الفلكية | |
| البعد | ~5,000 س.ض (1,580[2] ف.ف) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | −8.18[4] |
| تفاصيل | |
| نصف قطر | 1,420 (2,850?)[4] نق☉ |
| إضاءة (بولومتر) | 138,000,[2] 270,000 (1,100,000?)[4] ض☉ |
| جاذبية سطحية (log g) | −0.5 (−0.9?)[4] سم.غ.ثا |
| درجة الحرارة | 3,500[4] ك |
| تسميات اخرى | |
| تسمية النجوم المتغيرة Cyg, GSC 03152-01140, إبراس 20241+3811, IRC+40415, هيباركوس 3152-1140-1, RAFGL 2575, UCAC2 45230193, مسح ميكروي ثنائي لكامل السماء J20255805+3821076 | |
| قاعدة بيانات المراجع | |
| تعديل مصدري - تعديل | |
كي واي الدجاجة (بالإنجليزية: KY Cygni) عملاق أحمر ضخم تصنيف نجمي M3.5Ia يقع في كوكبة الدجاجة وهو واحد من أكبر النجوم المعروفة، مع قطر يقدر 1420 نصف قطر الشمس وهو أيضا من اشد النجوم ضياء 300،000 مرة أو أكثر من لمعان الشمس يقدر بعدة عنا بحوالي 5.200 سنة ضوئية.[6]
يقع كي واي الدجاجة بالقرب من العنقود المفتوح مسييه 29 ، ولكن لا يعتقد انة عضو في العنقود .فموقعة اقرب إلى نجم صدر الدجاجة .[7] تم التعرف عليه كنجم متغير في عام 1930,[8] وسمي فيما بعد باسم كي واي الدجاجة.[9]
مراجع
[عدل]- ^ ا ب Cutri، R. M.؛ Skrutskie، M. F.؛ Van Dyk، S.؛ Beichman، C. A.؛ Carpenter، J. M.؛ Chester، T.؛ Cambresy، L.؛ Evans، T.؛ Fowler، J.؛ Gizis، J.؛ Howard، E.؛ Huchra، J.؛ Jarrett، T.؛ Kopan، E. L.؛ Kirkpatrick، J. D.؛ Light، R. M.؛ Marsh، K. A.؛ McCallon، H.؛ Schneider، S.؛ Stiening، R.؛ Sykes، M.؛ Weinberg، M.؛ Wheaton، W. A.؛ Wheelock، S.؛ Zacarias، N. (2003). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: 2MASS All-Sky Catalog of Point Sources (Cutri+ 2003)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: II/246. Originally published in: University of Massachusetts and Infrared Processing and Analysis Center. ج. 2246: 0. Bibcode:2003yCat.2246....0C.
- ^ ا ب ج د ه Mauron، N.؛ Josselin، E. (2011). "The mass-loss rates of red supergiants and the de Jager prescription". Astronomy and Astrophysics. ج. 526: A156. arXiv:1010.5369. Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.156M. DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/201013993.
- ^ Alfonso-Garzón، J.؛ Domingo، A.؛ Mas-Hesse، J. M.؛ Giménez، A. (2012). "The first INTEGRAL-OMC catalogue of optically variable sources". Astronomy & Astrophysics. ج. 1210: arXiv:1210.0821. arXiv:1210.0821. Bibcode:2012A&A...548A..79A. DOI:10.1051/0004-6361/201220095.
{{استشهاد بدورية محكمة}}: الوسيط غير المعروف|class=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - ^ ا ب ج د ه و Levesque، Emily M.؛ Massey، Philip؛ Olsen، K. A. G.؛ Plez، Bertrand؛ Josselin، Eric؛ Maeder، Andre؛ Meynet، Georges (2005). "The Effective Temperature Scale of Galactic Red Supergiants: Cool, but Not As Cool As We Thought". The Astrophysical Journal. ج. 628 ع. 2: 973–985. arXiv:astro-ph/0504337. Bibcode:2005ApJ...628..973L. DOI:10.1086/430901.
- ^ ا ب KY Cyg, database entry, The combined table of GCVS Vols I-III and NL 67-78 with improved coordinates, General Catalogue of Variable Stars, Sternberg Astronomical Institute, Moscow, Russia. Accessed on line November 12, 2010. نسخة محفوظة 20 يونيو 2017 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- ^ Big and Giant Stars: KY Cygni نسخة محفوظة 11 يونيو 2018 على موقع واي باك مشين.
- ^ Romano، G. (1969). "Researches with the Schmidt telescopes. III. Variable stars in the field of gamma Cygni". Memorie della Società Astronomia Italiana. ج. 40: 375. Bibcode:1969MmSAI..40..375R.
- ^ Hoffmeister، Cuno (1930). "Relative Koordinaten, Oerter und Karten neuer Veraenderlicher". Mitteilungen der Sternwarte zu Sonneberg. ج. 17: 1. Bibcode:1930MiSon..17....1H.
- ^ Ahnert، P.؛ Van Schewick، H.؛ Hoffmeister، C. (1941). "Die Veraenderlichen Sterne der noerdlichen Milchstrasse. Teil II". Kleine Veroeffentlichungen der Universitaetssternwarte zu Berlin Babelsberg. ج. 6: 4.1. Bibcode:1941KVeBB...6....4A.