यूनाइटेड नेशंस के सदस्य देस
एह लेख के भोजपुरी में अनुवाद के जरूरत बाटे। ई लेख (या एकर कुछ हिस्सा) भोजपुरी की अलावे दूसर भाषा में लिखल बा। |


यूनाइटेड नेशंस के सदस्य देस 193 गो संप्रभु राज्य बाड़ऽसन that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the UN General Assembly.[2] The UN is the world's largest intergovernmental organization.
The criteria for admission of new members to the UN are set out in Chapter II, Article 4 of the UN Charter:[3]
- Membership in the United Nations is open to all peace-loving states which accept the obligations contained in the present Charter and, in the judgement of the Organization, are able and willing to carry out these obligations.
- The admission of any such state to membership in the United Nations will be effected by a decision of the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council.
A recommendation for admission from the Security Council requires affirmative votes from at least nine of the council's fifteen members, with none of the five permanent members using their veto power. The Security Council's recommendation must then be approved in the General Assembly by a two-thirds majority vote.[4]
In principle, only sovereign states can become UN members, and currently all UN members are sovereign states. Although five members were not sovereign when they joined the UN, all subsequently became fully independent between 1946 and 1991. Because a state can only be admitted to membership in the UN by the approval of the Security Council and the General Assembly, a number of states that are considered sovereign according to the Montevideo Convention are not members of the UN. This is because the UN does not consider them to possess sovereignty, mainly due to the lack of international recognition or due to opposition from one of the permanent members.
In addition to the member states, the UN also invites non-member states to become observers at the UN General Assembly (currently two: the Holy See and Palestine), allowing them to participate and speak in General Assembly meetings, but not vote. Observers are generally intergovernmental organizations and international organizations and entities whose statehood or sovereignty is not precisely defined.
मूल सदस्य देस सभ
[संपादन करीं]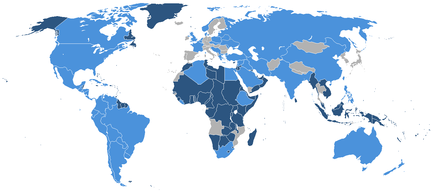

The UN officially came into existence on 24 October 1945, after ratification of the United Nations Charter by the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council (the Republic of China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States) and a majority of the other signatories.[6] A total of 51 original members (or founding members) joined that year; 50 of them signed the Charter at the United Nations Conference on International Organization in San Francisco on 26 June 1945, while Poland, which was not represented at the conference, signed it on 15 October 1945.[7][8]
The original members of the United Nations were: France, the Republic of China, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, the United States, Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Bolivia, Brazil, Byelorussia, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Czechoslovakia, Denmark, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Egypt, El Salvador, Ethiopia, Greece, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, India, Iran, Iraq, Lebanon, Liberia, Luxembourg, Mexico, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Nicaragua, Norway, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, the Philippines, Poland, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Syria, Turkey, Ukraine, Uruguay, Venezuela and Yugoslavia.[8]
Among the original members, 49 are either still UN members or had their memberships in the UN continued by a successor state (see table below); for example, the membership of the Soviet Union was continued by the Russian Federation after its dissolution (see the section Former members: Union of Soviet Socialist Republics). The other two original members, Czechoslovakia and Yugoslavia (i.e., the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia), had been dissolved and their memberships in the UN not continued from 1992 by any one successor state (see the sections Former members: Czechoslovakia and Former members: Yugoslavia).[8]
At the time of UN's founding, the seat of China in the UN was held by the Republic of China, but as a result of United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758 in 1971, it is now held by the People's Republic of China (see the section Former members: Republic of China (Taiwan)).
A number of the original members were not sovereign when they joined the UN, and only gained full independence later:[9]
- Belarus (then the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic) and Ukraine (then the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic) were both constituent republics of the Soviet Union, until gaining full independence in 1991.
- भारत (whose territory at that time, before the Partition of India, also included the present-day territories of Pakistan and Bangladesh) was under British colonial rule, until gaining full independence in 1947.
- The Philippines (then the Philippine Commonwealth) was a commonwealth with the United States, until gaining full independence in 1946.
- New Zealand, while de facto sovereign at that time, "only gained full capacity to enter into relations with other states in 1947 when it passed the Statute of Westminster Adoption Act. This occurred 16 years after the British Parliament passed the Statute of Westminster Act in 1931 that recognised New Zealand's autonomy. If judged by the Montevideo Convention criteria, New Zealand did not achieve full de jure statehood until 1947."[10]
वर्तमान मेंबर सभ
[संपादन करीं]वर्तमान सदस्य लोग आ इनहन के प्रवेश के तारीख नीचे दिहल गइल बा आ इनहन के आधिकारिक नाँव दिहल गइल बा जेकर इस्तेमाल संयुक्त राष्ट्र द्वारा कइल जाला।[11][12]
The alphabetical order by the member states' official designations is used to determine the seating arrangement of the General Assembly sessions, where a draw is held each year to select a member state as the starting point.[13] Several members use their full official names in their official designations and thus are sorted out of order from their common names: the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of Korea, the Republic of Moldova and the United Republic of Tanzania.
The member states can be sorted by their official designations and dates of admission by clicking on the buttons in the header of the columns. See related sections on former members by clicking on the links in the column See also.
Original members are listed with blue background.
पुरान सदस्य सभ
[संपादन करीं]चीन रिपब्लिक
[संपादन करीं]
The Republic of China (ROC) joined the UN as an original member on 24 October 1945, and as set out by the United Nations Charter, Chapter V, Article 23, became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.[17] In 1949, as a result of the Chinese Civil War, the Kuomintang-led ROC government lost effective control of mainland China and relocated to the island of Taiwan, and the Communist Party-led government of the People's Republic of China (PRC), declared on 1 October 1949, took control of mainland China. The UN was notified on 18 November 1949 of the formation of the Central People's Government of the People's Republic of China; however, the Government of the Republic of China continued to represent China at the UN, despite the small size of the ROC's jurisdiction of Taiwan and a number of smaller islands compared to the PRC's jurisdiction of mainland China. As both governments claimed to be the sole legitimate representative of China, proposals to effect a change in the representation of China in the UN were discussed but rejected for the next two decades, as the ROC was still recognized as the sole legitimate representative of China by a majority of UN members.[प्रमाण देईं] Both sides rejected compromise proposals to allow both states to participate in the UN, based on the One-China policy.[18]
By the 1970s, a shift had occurred in international diplomatic circles and the PRC had gained the upper hand in international diplomatic relations and recognition count. On 25 October 1971, the 21st time the United Nations General Assembly debated on the PRC's admission into the UN,[19] United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758 was adopted, by which it recognized that "the representatives of the Government of the People's Republic of China are the only lawful representatives of China to the United Nations and that the People's Republic of China is one of the five permanent members of the Security Council," and decided "to restore all its rights to the People's Republic of China and to recognize the representatives of its Government as the only legitimate representatives of China to the United Nations, and to expel forthwith the representatives of Chiang Kai-shek from the place which they unlawfully occupy at the United Nations and in all the organizations related to it."[20] This effectively transferred the seat of China in the UN, including its permanent seat on the Security Council, from the ROC to the PRC, and expelled the ROC from the UN. From the United Nations' perspective the "Republic of China" is not a former member. No UN member was expelled in 1971. Rather, the credentials of one Chinese delegation (from Taipei) were rejected and the credentials of another Chinese delegation (from Beijing) were accepted.[प्रमाण देईं]
In addition to losing its seat in the UN, the UN Secretary-General concluded from the resolution that the General Assembly considered Taiwan to be a province of China. Consequently, the Secretary-General decided that it was not permitted for the ROC to become a party to treaties deposited with it.[21]
Bids for readmission as the representative of Taiwan
[संपादन करीं]
In 1993 the ROC began campaigning to rejoin the UN separately from the People's Republic of China. A number of options were considered, including seeking membership in the specialized agencies, applying for observer status, applying for full membership, or having resolution 2758 revoked to reclaim the seat of China in the UN.[22]
Every year from 1993–2006, UN member states submitted a memorandum to the UN Secretary-General requesting that the UN General Assembly consider allowing the ROC to resume participating in the United Nations.[23] This approach was chosen, rather than a formal application for membership, because it could be enacted by the General Assembly, while a membership application would need Security Council approval, where the PRC held a veto.[22] Early proposals recommended admitting the ROC with parallel representation over China, along with the People's Republic of China, pending eventual reunification, citing examples of other divided countries which had become separate UN member states, such as East and West Germany and North and South Korea. Later proposals emphasized that the ROC was a separate state, over which the PRC had no effective sovereignty. These proposed resolutions referred to the ROC under a variety of names: "Republic of China in Taiwan" (1993–94), "Republic of China on Taiwan" (1995–97, 1999–2002), "Republic of China" (1998), "Republic of China (Taiwan)" (2003) and "Taiwan" (2004–06).
However, all fourteen attempts were unsuccessful as the General Assembly's General Committee declined to put the issue on the Assembly's agenda for debate, under strong opposition from the PRC.[24]
While all these proposals were vague, requesting the ROC be allowed to participate in UN activities without specifying any legal mechanism, in 2007 the ROC submitted a formal application under the name "Taiwan" for full membership in the UN.[25] However, the application was rejected by the United Nations Office of Legal Affairs citing General Assembly Resolution 2758,[26] without being forwarded to the Security Council. Secretary-General of the United Nations Ban Ki-moon stated that:
The position of the United Nations is that the People's Republic of China is representing the whole of China as the sole and legitimate representative Government of China. The decision until now about the wish of the people in Taiwan to join the United Nations has been decided on that basis. The resolution (General Assembly Resolution 2758) that you just mentioned is clearly mentioning that the Government of China is the sole and legitimate Government and the position of the United Nations is that Taiwan is part of China.[27]
Responding to the UN's rejection of its application, the ROC government has stated that Taiwan is not now nor has it ever been under the jurisdiction of the PRC, and that since General Assembly Resolution 2758 did not clarify the issue of Taiwan's representation in the UN, it does not prevent Taiwan's participation in the UN as an independent sovereign nation.[28] The ROC government also criticized Ban for asserting that Taiwan is part of China and returning the application without passing it to the Security Council or the General Assembly,[29] contrary to UN's standard procedure (Provisional Rules of Procedure of the Security Council, Chapter X, Rule 59).[30] On the other hand, the PRC government, which has stated that Taiwan is part of China and firmly opposes the application of any Taiwan authorities to join the UN either as a member or an observer, praised that UN's decision "was made in accordance with the UN Charter and Resolution 2758 of the UN General Assembly, and showed the UN and its member states' universal adherence to the one-China principle".[31] A group of UN member states put forward a draft resolution for that fall's UN General Assembly calling on the Security Council to consider the application.[25]
The following year two referendums in Taiwan on the government's attempts to regain participation at the UN did not pass due to low turnout. That fall the ROC took a new approach, with its allies submitting a resolution requesting that the "Republic of China (Taiwan)" be allowed to have "meaningful participation" in the UN specialized agencies.[32] Again the issue was not put on the Assembly's agenda.[24] In 2009, the ROC chose not to bring the issue of its participation in the UN up for debate at the General Assembly for the first time since it began the campaign in 1993.[33]
In May 2009, the Department of Health of the Republic of China was invited by the World Health Organization to attend the 62nd World Health Assembly as an observer under the name "Chinese Taipei". This was the ROC's first participation in an event organized by a UN-affiliated agency since 1971, as a result of the improved cross-strait relations since Ma Ying-jeou became the President of the Republic of China a year before.[34]
The Republic of China is officially recognized by 21 UN member states and the Holy See. It maintains unofficial diplomatic relations with around 100 nations, including the United States and Japan.
चेकोस्लोवाकिया
[संपादन करीं]Czechoslovakia joined the UN as an original member on 24 October 1945, with its name changed to the Czech and Slovak Federative Republic on 20 April 1990. Upon the imminent dissolution of Czechoslovakia, in a letter dated 10 December 1992, its Permanent Representative informed the United Nations Secretary-General that the Czech and Slovak Federative Republic would cease to exist on 31 December 1992 and that the Czech Republic and Slovakia, as successor states, would apply for membership in the UN. Neither state sought sole successor state status. Both states were admitted to the UN on 19 January 1993.[35]
जर्मन डेमोक्रेटिक रिपब्लिक
[संपादन करीं]Both the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany) and the German Democratic Republic (East Germany) were admitted to the UN on 18 September 1973. Through the accession of the East German federal states to the Federal Republic of Germany, effective from 3 October 1990, the territory of the German Democratic Republic became part of the Federal Republic of Germany, today simply known as Germany. Consequently, the Federal Republic of Germany continued being a member of the UN while the German Democratic Republic ceased to exist.[35]
मलाया फेडरेशन
[संपादन करीं]The Federation of Malaya joined the United Nations on 17 September 1957. On 16 September 1963, its name was changed to Malaysia, following the formation of Malaysia from Singapore, North Borneo (now Sabah), Sarawak and the Federation of Malaya. Singapore became an independent State on 9 August 1965 and a Member of the United Nations on 21 September 1965.
टैंगानिका आ जंजीबार
[संपादन करीं]Tanganyika was admitted to the UN on 14 December 1961, and Zanzibar was admitted to the UN on 16 December 1963. Following the ratification on 26 April 1964 of the Articles of Union between Tanganyika and Zanzibar, the two states merged to form the single member "United Republic of Tanganyika and Zanzibar", with its name changed to the United Republic of Tanzania on 1 November 1964.[35][5]
यूएसएसआर
[संपादन करीं]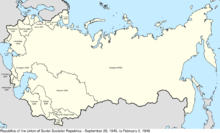
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) joined the UN as an original member on 24 October 1945, and as set out by the United Nations Charter, Chapter V, Article 23, became one of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.[17] Upon the imminent dissolution of the USSR, in a letter dated 24 December 1991, Boris Yeltsin, the President of the Russian Federation, informed the United Nations Secretary-General that the membership of the USSR in the Security Council and all other UN organs was being continued by the Russian Federation with the support of the 11 member countries of the Commonwealth of Independent States.[35]
The other fourteen independent states established from the former Soviet Republics were all admitted to the UN:
- The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic and the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic joined the UN on 24 October 1945 together with the USSR. After declaring independence, the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic changed its name to Ukraine on 24 August 1991, and on 19 September 1991, the Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic informed the UN that it had changed its name to Belarus.
- Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania were admitted to the UN on 17 September 1991, after regaining independence before the dissolution of the USSR.
- Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Republic of Moldova, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan were admitted to the UN on 2 March 1992.
- Georgia was admitted to the UN on 31 July 1992.
यूनाइटेड अरब रिपब्लिक
[संपादन करीं]
Both Egypt and Syria joined the UN as original members on 24 October 1945. Following a plebiscite on 21 February 1958, the United Arab Republic was established by a union of Egypt and Syria and continued as a single member. On 13 October 1961, Syria, having resumed its status as an independent state, resumed its separate membership in the UN. Egypt continued as a UN member under the name of the United Arab Republic, until it reverted to its original name on 2 September 1971. Syria changed its name to the Syrian Arab Republic on 14 September 1971.[35]
Yemen and Democratic Yemen
[संपादन करीं]Yemen (i.e., North Yemen) was admitted to the UN on 30 September 1947; Southern Yemen (i.e., South Yemen) was admitted to the UN on 14 December 1967, with its name changed to the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen on 30 November 1970, and was later referred to as Democratic Yemen. On 22 May 1990, the two states merged to form the Republic of Yemen, which continued as a single member under the name Yemen.[35]
यूगोस्लाविया
[संपादन करीं]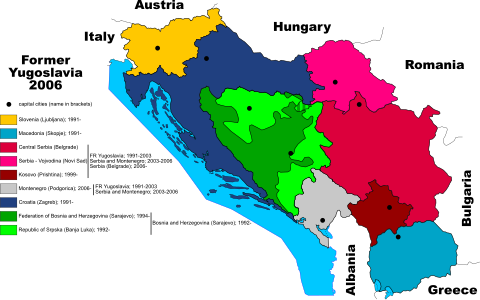
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, referred to as Yugoslavia, joined the UN as an original member on 24 October 1945. By 1992, it had been effectively dissolved into five independent states, which were all subsequently admitted to the UN:
- Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and Slovenia were admitted to the UN on 22 May 1992.[36]
- Macedonia was admitted to the UN on 8 April 1993, being provisionally referred to for all purposes within the UN as "The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia" pending settlement of the difference that had arisen over its name.[37]
- The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (name later changed to Serbia and Montenegro) was admitted to the UN on 1 November 2000.[38]
Due to the dispute over its legal successor states, the member state "Yugoslavia", referring to the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, remained on the official roster of UN members for many years after its effective dissolution.[35] Following the admission of all five states as new UN members, "Yugoslavia" was removed from the official roster of UN members.
The government of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, established on 28 April 1992 by the remaining Yugoslav republics of Montenegro and Serbia,[39] claimed itself as the legal successor state of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia;[40] however, on 30 May 1992, United Nations Security Council Resolution 757 was adopted, by which it imposed international sanctions on the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia due to its role in the Yugoslav Wars, and noted that "the claim by the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) to continue automatically the membership of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in the United Nations has not been generally accepted,"[41] and on 22 September 1992, United Nations General Assembly Resolution A/RES/47/1 was adopted, by which it considered that "the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) cannot continue automatically the membership of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in the United Nations," and therefore decided that "the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) should apply for membership in the United Nations and that it shall not participate in the work of the General Assembly".[42][43] The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia refused to comply with the resolution for many years, but following the ousting of President Slobodan Milošević from office, it applied for membership, and was admitted to the UN on 1 November 2000.[38] On 4 February 2003, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia had its official name changed to Serbia and Montenegro, following the adoption and promulgation of the Constitutional Charter of Serbia and Montenegro by the Assembly of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia.[44]
On the basis of a referendum held on 21 May 2006, Montenegro declared independence from Serbia and Montenegro on 3 जून 2006. In a letter dated on the same day, the President of Serbia informed the United Nations Secretary-General that the membership of Serbia and Montenegro in the UN was being continued by Serbia, following Montenegro's declaration of independence, in accordance with the Constitutional Charter of Serbia and Montenegro.[45] Montenegro was admitted to the UN on 28 जून 2006.[46]
In the aftermath of the Kosovo War, the territory of Kosovo, then an autonomous province of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, was put under the interim administration of the United Nations Mission in Kosovo on 10 June 1999. On 17 February 2008 it declared independence, but this has not been recognised by Serbia. The Republic of Kosovo is not a member of the UN, but is a member of the International Monetary Fund[47] and the World Bank Group,[48] both specialized agencies in the United Nations System. The Republic of Kosovo is recognised by 108 UN member states, including three of the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council (France, the United Kingdom, and the United States), while the other two—China and Russia—do not recognise Kosovo. On 22 July 2010, the International Court of Justice, the primary judicial organ of the UN, issued an advisory opinion, ruling that Kosovo's declaration of independence was not in violation of international law.[49]
Suspension, expulsion, and withdrawal of members
[संपादन करीं]A member state may be suspended or expelled from the UN, according to the United Nations Charter. From Chapter II, Article 5:[3]
A Member of the United Nations against which preventive or enforcement action has been taken by the Security Council may be suspended from the exercise of the rights and privileges of membership by the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council. The exercise of these rights and privileges may be restored by the Security Council.
From Article 6:[3]
A Member of the United Nations which has persistently violated the Principles contained in the present Charter may be expelled from the Organization by the General Assembly upon the recommendation of the Security Council.
Since its inception, no member state has been suspended or expelled from the UN under Articles 5 and 6. However, in a few cases, states were suspended or expelled from participating in UN activities by means other than Articles 5 and 6:
- On 25 October 1971, United Nations General Assembly Resolution 2758 was adopted, which recognized the People's Republic of China instead of the Republic of China (since 1949 controlling only Taiwan) as the legitimate representative of China in the UN and effectively expelled the Republic of China from the UN in 1971 (see the section Former members: Republic of China). This act did not constitute as the expulsion of a member state under Article 6, as this would have required Security Council approval and been subjected to vetoes by its permanent members, which included the Republic of China itself and the United States, which at that time still recognized the Republic of China.[50]
- In October 1974, the Security Council considered a draft resolution that would have recommended that the General Assembly immediately expel South Africa from the UN, in compliance with Article 6 of the United Nations Charter, due to its apartheid policies.[35] However, the resolution was not adopted because of vetoes by three permanent members of the Security Council: France, the United Kingdom, and the United States. In response, the General Assembly decided to suspend South Africa from participation in the work of the Assembly's 29th session on 12 November 1974; however, South Africa was not formally suspended under Article 5. The suspension lasted until the General Assembly welcomed South Africa back to full participation in the UN on 23 June 1994, following its successful democratic elections earlier that year.[51]
- On 28 April 1992, the new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was established, by the remaining republics of Serbia and Montenegro of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. On 22 September 1992, United Nations General Assembly Resolution A/RES/47/1 was adopted, by which it considered that "the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) cannot continue automatically the membership of the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in the United Nations," and therefore decided that "the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Serbia and Montenegro) should apply for membership in the United Nations and that it shall not participate in the work of the General Assembly". It did not apply for membership until Slobodan Milošević was ousted from the presidency and was admitted on 1 November 2000 (see the section Former members: Yugoslavia).
Withdrawal of Indonesia (1965–1966)
[संपादन करीं]
Since the inception of the UN, only one member state (excluding those that dissolved or merged with other member states) has unilaterally withdrawn from the UN. During the Indonesia–Malaysia confrontation, and in response to the election of Malaysia as a non-permanent member of the United Nations Security Council, in a letter dated 20 January 1965, Indonesia informed the United Nations Secretary-General that it had decided "at this stage and under the present circumstances" to withdraw from the UN. However, following the overthrow of President Sukarno, in a telegram dated 19 September 1966, Indonesia notified the Secretary-General of its decision "to resume full cooperation with the United Nations and to resume participation in its activities starting with the twenty-first session of the General Assembly". On 28 September 1966, the United Nations General Assembly took note of the decision of the Government of Indonesia and the President invited the representatives of that country to take their seats in the Assembly.[35]
Unlike suspension and expulsion, no express provision is made in the United Nations Charter of whether or how a member can legally withdraw from the UN (largely to prevent the threat of withdrawal from being used as a form of political blackmail, or to evade obligations under the Charter, similar to withdrawals that weakened the UN's predecessor, the League of Nations),[50] or on whether a request for readmission by a withdrawn member should be treated the same as an application for membership, i.e., requiring Security Council as well as General Assembly approval. Indonesia's return to the UN would suggest that this is not required; however, scholars have argued that the course of action taken by the General Assembly was not in accordance with the Charter from a legal point of view.[52]
Observers and non-members
[संपादन करीं]
In addition to the member states, there are two non-member permanent observer states: the Holy See and the State of Palestine.[53]
- The Holy See holds sovereignty over the state of Vatican City and maintains diplomatic relations with 180 other states. It has been an observer state since 6 April 1964,[54] and gained all the rights of full membership except voting on 1 July 2004.[55]
- The Palestine Liberation Organization was granted observer status as a "non-member entity" on 22 November 1974.[56] Acknowledging the proclamation of the State of Palestine by the Palestine National Council on 15 November 1988, the United Nations General Assembly decided that, effective as of 15 December 1988, the designation "Palestine" should be used in place of the designation "Palestine Liberation Organization" in the United Nations System.[57] On 23 September 2011, Palestinian National Authority President Mahmoud Abbas submitted the application for UN membership for the State of Palestine to United Nations Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon;[58][59] the application has not been voted on by the UN Security Council. On 31 अक्टूबर 2011, the General Assembly of UNESCO voted to admit Palestine as a member, becoming the first UN agency to admit Palestine as a full member.[60] The State of Palestine was recognized as a "non-member state" on 29 November 2012, when the UN General Assembly passed United Nations General Assembly resolution 67/19 by a vote of 138 to 9, with 41 abstentions.[61][62][63] The change in status was described by The Independent as "de facto recognition of the sovereign state of Palestine".[64] On 17 December 2012, UN Chief of Protocol Yeocheol Yoon decided that "the designation of 'State of Palestine' shall be used by the Secretariat in all official United Nations documents".[53]
The Sovereign Military Order of Malta, while not a state, has observer status at the UN and maintains diplomatic relations with 107 countries.[65][66]
A number of states were also granted observer status before being admitted to the UN as full members.[67][68][69] The most recent case of an observer state becoming a member state was Switzerland, which was admitted in 2002.[70]
A European Union institution, the European Commission, was granted observer status at the UNGA through Resolution 3208 in 1974. The Treaty of Lisbon in 2009 resulted in the delegates being accredited directly to the EU.[71] It was accorded full rights in the General Assembly, bar the right to vote and put forward candidates, via UNGA Resolution A/RES/65/276 on 10 May 2011.[72] It is the only non-state party to over 50 multilateral conventions, and has participated as a full member in every way except for having a vote in a number of UN conferences.[73]
The sovereignty status of Western Sahara is in dispute between Morocco and the Polisario Front. Most of the territory is controlled by Morocco, the remainder (the Free Zone) by the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, proclaimed by the Polisario Front. Western Sahara is listed by the UN as a "non-self-governing territory".[74]
The Cook Islands and Niue, which are both associated states of New Zealand, are not members of the UN, but are members of specialized agencies of the UN such as WHO[75] and UNESCO,[76] and have had their "full treaty-making capacity" recognized by United Nations Secretariat in 1992 and 1994 respectively.[77][78] They have since become parties to a number of international treaties which the UN Secretariat acts as a depositary for, such as the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change[79] and the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea,[80] and are treated as non-member states.[81][77] Both the Cook Islands and Niue have expressed a desire to become a UN member state, but New Zealand has said that they would not support the application without a change in their constitutional relationship, in particular their right to New Zealand citizenship.[82][83]
नोट
[संपादन करीं]- ↑ Benin: Name was changed from Dahomey on 1 December 1975.
- ↑ Bolivia (Plurinational State of): Previously referred to as Bolivia.
- ↑ Burkina Faso: Name was changed from Upper Volta on 6 August 1984.
- ↑ Cabo Verde: Previously referred to as Cape Verde. On 24 अक्टूबर 2013, Cabo Verde requested that its name no longer be translated into different languages.[15]
- ↑ Cambodia: Name was changed to the Khmer Republic on 7 October 1970, and back to Cambodia on 30 April 1975. Name was changed again to Democratic Kampuchea on 6 April 1976, and back to Cambodia on 3 February 1990.
- ↑ Cameroon: Previously referred to as Cameroun (before merging with Southern Cameroons in 1961). By a letter of 4 January 1974, the Secretary-General was informed that Cameroon had changed its name to the United Republic of Cameroon. Name was changed back to Cameroon on 4 February 1984.
- ↑ Central African Republic: By a letter of 20 December 1976, the Central African Republic advised that it had changed its name to the Central African Empire. Name was changed back to the Central African Republic on 20 September 1979.
- ↑ Congo: Previously referred to as Congo (Brazzaville) (to differentiate it from Congo (Leopoldville)) and the People's Republic of the Congo. Name was changed to Congo on 15 November 1971 (after the Democratic Republic of the Congo changed its name to Zaire). Also referred to as Congo (Republic of the).
- ↑ Côte d'Ivoire: Previously referred to as Ivory Coast. On 6 November 1985, Côte d'Ivoire requested that its name no longer be translated into different languages; this became fully effective on 1 January 1986.
- ↑ Democratic Republic of the Congo: Previously referred to as Congo (Leopoldville) (to differentiate it from Congo (Brazzaville)). Name was changed from the Democratic Republic of the Congo to Zaire on 27 October 1971, and back to the Democratic Republic of the Congo on 17 May 1997.
- ↑ Eswatini: Name was changed from Swaziland on 18 April 2018.
- ↑ Gambia: Previously referred to as The Gambia.
- ↑ Withdrew from the UN on 20 January 1965. It rejoined on 28 September 1966.
- ↑ Iran (Islamic Republic of): Previously referred to as Iran. By a communication of 5 March 1981, Iran informed the Secretary-General that it should be referred to by its complete name of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
- ↑ Kazakhstan: Spelling was changed from Kazakstan on 20 June 1997.
- ↑ Lao People's Democratic Republic: Name was changed from Laos on 2 December 1975.
- ↑ Libya: Formerly recognised as the Libyan Arab Republic from 1969 after originally being admitted as Libya. By notes verbales of 1 and 21 April 1977, the Libyan Arab Republic advised that it had changed its name to the Libyan Arab Jamahiriya. On 16 September 2011, the UN General Assembly awarded the UN seat to the National Transitional Council, thereby restoring the original name of Libya.
- ↑ Madagascar: Previously referred to as the Malagasy Republic.
- ↑ Maldives: Previously referred to as the Maldive Islands.
- ↑ Myanmar: Name was changed from Burma on 18 June 1989.
- ↑ North Macedonia: Name was changed from Republic of Macedonia on 12 February 2019.
- ↑ Philippines: Previously referred to as the Philippine Commonwealth (before becoming a republic in 1946) and as the Philippine Republic.
- ↑ Republic of Moldova: Previously referred to as Moldova.
- ↑ Saint Kitts and Nevis: Name was changed officially from Saint Christopher and Nevis on 26 November 1986; the UN, however, continued to use the former name throughout the year.
- ↑ Sao Tome and Principe: The official UN designation lacks diacritics; however, the name is constitutionally defined as São Tomé and Príncipe, with diacritics.
- ↑ South Africa: Previously referred to as the Union of South Africa (before becoming a republic in 1961).
- ↑ Sri Lanka: Name was changed from Ceylon on 22 May 1972.
- ↑ Suriname: Name was changed from Surinam on 23 January 1978.
- ↑ Thailand: Previously referred to as Siam.
- ↑ Venezuela (Bolivarian Republic of): Previously referred to as Venezuela.
संदर्भ
[संपादन करीं]- ↑ "The World" (PDF). United Nations. The following territories are excluded as the UN does not consider them as part of any member state: Vatican City (the Holy See is a UN non-member observer state), the Palestinian territories (Palestine is a UN non-member observer state), Western Sahara (status in dispute between Morocco and the Polisario Front), and Antarctica (regulated by the Antarctic Treaty System). Territories of states not recognized by the UN are not excluded due to the UN's position that they are part of some UN member state, including, for example, the territories governed by the Republic of China (Taiwan and other smaller islands), as the UN members voted to consider the People's Republic of China as the only lawful representative of China at the UN and the UN chooses not to question its claim that Taiwan is part of China.
- ↑ "What are Member States?". United Nations.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Charter of the United Nations, Chapter II: Membership". United Nations.
- ↑ "About UN Membership". United Nations.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Growth in United Nations membership, 1945–present". United Nations.
- ↑ "History of the United Nations". United Nations.
- ↑ "Founding Member States". United Nations.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 "CHAPTER I – CHARTER OF THE UNITED NATIONS AND STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL COURT OF JUSTICE". United Nations. Retrieved 2015-10-07.
- ↑ "The World in 1945" (PDF). United Nations.
- ↑ John Wilson (अगस्त 2007). "New Zealand Sovereignty: 1857, 1907, 1947, or 1987?". New Zealand Parliament. Archived from the original on 22 मई 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ "Current Member States". United Nations.
- ↑ "Blue Book "Permanent Missions to the United Nations No. 306"" (PDF). United Nations. जून 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 31 अक्टूबर 2018. Retrieved 19 फरवरी 2018.
- ↑ "Thailand's name picked to set seating arrangement for General Assembly session". United Nations. 2 अगस्त 2005.
- ↑ "CHAPTER I – CHARTER OF THE UNITED NATIONS AND STATUTE OF THE INTERNATIONAL COURT OF JUSTICE". United Nations. Retrieved 2015-10-07.
- ↑ "Change of name – Cape Verde" (PDF). United Nations. 29 अक्टूबर 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 जनवरी 2014. Retrieved 2 जनवरी 2014.
- ↑ Lederer, Edith M. (16 September 2011). "UN approves Libya seat for former rebels". Google News. Associated Press. Retrieved 16 September 2011.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 "Charter of the United Nations, Chapter V: The Security Council". United Nations.
- ↑ Winkler, Sigrid (जून 2012). "Taiwan's UN Dilemma: To Be or Not To Be". Brookings Institution. Retrieved 2016-04-25.
- ↑ "1971 Year in Review: Red China Admitted to UN". United Press International. 1971.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 26 Resolution 2758. Restoration of the lawful rights of the People's Republic of China in the United Nations A/RES/2758(XXVI) page 1. 25 October 1971. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ "FINAL CLAUSES OF MULTILATERAL TREATIES" (PDF). United Nations. 2003. Retrieved 2016-04-25.
Hence, instruments received from the Taiwan Province of China will not be accepted by the Secretary-General in his capacity as depositary.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Lindemann, Björn Alexander (2014). Cross-Strait Relations and International Organizations: Taiwan’s Participation in IGOs in the Context of Its Relationship with China. Springer Science+Business Media. p. 258.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 48 Agenda item REQUEST FOR THE INCLUSION OF A SUPPLEMENTARY ITEM IN THE AGENDA OF THE FORTY-EIGHTH SESSION CONSIDERATION OF THE EXCEPTIONAL SITUATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN TAIWAN IN THE INTERNATIONAL CONTEXT, BASED ON THE PRINCIPLE OF UNIVERSALITY AND IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE ESTABLISHED MODEL OF PARALLEL REPRESENTATION OF DIVIDED COUNTRIES AT THE UNITED NATIONS A/48/191 1993-08-09. Retrieved 2016-04-18.
United Nations General Assembly Session 49 Agenda item REQUEST FOR THE INCLUSION OF AN ITEM IN THE PROVISIONAL AGENDA OF THE FORTY-NINTH SESSION CONSIDERATION OF THE EXCEPTIONAL SITUATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF CHINA IN TAIWAN IN THE INTERNATIONAL CONTEXT, BASED ON THE PRINCIPLE OF UNIVERSALITY AND IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE ESTABLISHED MODEL OF PARALLEL REPRESENTATION OF DIVIDED COUNTRIES AT THE UNITED NATIONS A/49/144 1994-07-19. Retrieved 2016-04-18.
United Nations General Assembly Session 50 Agenda item REQUEST FOR THE INCLUSION OF AN ITEM IN THE PROVISIONAL AGENDA OF THE FIFTIETH SESSION CONSIDERATION OF THE EXCEPTIONAL SITUATION OF THE REPUBLIC OF CHINA ON TAIWAN IN THE INTERNATIONAL CONTEXT, BASED ON THE PRINCIPLE OF UNIVERSALITY AND IN ACCORDANCE WITH THE ESTABLISHED MODEL OF PARALLEL REPRESENTATION OF DIVIDED COUNTRIES AT THE UNITED NATIONS A/50/145 1995-07-19. Retrieved 2016-04-18.
United Nations General Assembly Session 51 Agenda item REQUEST FOR THE INCLUSION OF AN ITEM IN THE PROVISIONAL AGENDA OF THE FIFTY-FIRST SESSION CONSIDERATION OF THE EXCEPTIONAL SITUATION OF THE INABILITY, RESULTING FROM GENERAL ASSEMBLY RESOLUTION 2758 (XXVI), OF THE 21.3 MILLION PEOPLE ON TAIWAN, REPUBLIC OF CHINA, TO PARTICIPATE IN THE ACTIVITIES OF THE UNITED NATIONS A/51/142 1996-07-18. Retrieved 2016-04-19.
United Nations General Assembly Session 52 Agenda item REQUEST FOR THE INCLUSION OF AN ITEM IN THE PROVISIONAL AGENDA OF THE FIFTY-SECOND SESSION NEED TO REVIEW GENERAL ASSEMBLY RESOLUTION 2758 (XXVI) OF 25 OCTOBER 1971 OWING TO THE FUNDAMENTAL CHANGE IN THE INTERNATIONAL SITUATION AND TO THE COEXISTENCE OF TWO GOVERNMENTS ACROSS THE TAIWAN STRAIT A/52/143 1997-07-16. Retrieved 2016-04-19.
United Nations General Assembly Session 53 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of an item in the provisional agenda of the fifty-third session Need to review General Assembly resolution 2758 (XXVI) of 25 October 1971 owing to the fundamental change in the international situation and to the coexistence of two Governments across the Taiwan Strait A/53/145 1998-07-08. Retrieved 2016-04-19.
United Nations General Assembly Session 54 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-fourth session Need to examine the exceptional international situation pertaining to the Republic of China on Taiwan, to ensure that the fundamental right of its twenty-two million people to participate in the work and activities of the United Nations is fully respected A/54/194 1999-08-12. Retrieved 2016-04-20.
United Nations General Assembly Session 55 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-fifth session Need to examine the exceptional international situation pertaining to the Republic of China on Taiwan, to ensure that the fundamental right of its twenty-three million people to participate in the work and activities of the United Nations is fully respected A/55/227 2000-08-04. Retrieved 2016-04-23.
United Nations General Assembly Session 56 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-sixth session Need to examine the exceptional international situation pertaining to the Republic of China on Taiwan, to ensure that the fundamental right of its twenty-three million people to participate in the work and activities of the United Nations is fully respected A/56/193 2001-08-08. Retrieved 2016-04-23.
United Nations General Assembly Session 57 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-seventh session Question of the representation of the Republic of China (Taiwan) in the United Nations A/57/191 2002-08-20. Retrieved 2016-04-23.
United Nations General Assembly Session 58 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-eighth session Question of the representation of the Republic of China (Taiwan) in the United Nations A/58/197 2003-08-05. Retrieved 2016-04-23.
United Nations General Assembly Session 59 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the fifty-ninth session Question of the representation of the twenty-three million people of Taiwan in the United Nations A/59/194 2004-08-10. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
United Nations General Assembly Session 60 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the sixtieth session Question of the representation of the twenty-three million people of Taiwan in the United Nations A/60/192 2005-08-11. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
United Nations General Assembly Session 61 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the sixty-first session Question of the representation and participation of the 23 million people of Taiwan in the United Nations A/61/194 2006-08-11. Retrieved 2016-04-24. - ↑ 24.0 24.1 Damm, Jens; Lim, Paul (2012). European Perspectives on Taiwan. Springer Science+Business Media. pp. 160–63.
By mid 2009, 16 applications for membership on behalf of Taiwan had been sent to the UN, but, in each of these cases, the General Assembly's General Committee, which sets the Assembly's agenda, decided against even raising the question during the Assembly's session.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 United Nations General Assembly Session 62 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the sixty-second session Urging the Security Council to process Taiwan’s membership application pursuant to rules 59 and 60 of the provisional rules of procedure of the Security Council and Article 4 of the Charter of the United Nations A/62/193 2007-08-17. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ "Transcript: Daily Press Briefing by the Office of the Spokesperson for the Secretary-General". United Nations. 23 July 2007.
- ↑ "Ban Ki-moon Convenes Largest-Ever Meeting of Global Leaders on Climate Change". United Nations. 24 September 2007. Retrieved 2017-06-08.
- ↑ "Talking points for Taiwan's UN Membership Application". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China. Archived from the original on 9 जनवरी 2009.
- ↑ "President Chen Shui-bian's Letters to UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon and UN Security Council President Wang Guangya on July 31 (Office of the President)". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Republic of China. Archived from the original on 4 सितंबर 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ "Provisional Rules of Procedure of the Security Council". United Nations.
- ↑ "China praises UN's rejection of Taiwan's application for membership". Xinhua News Agency. 24 जुलाई 2007. Archived from the original on 11 जनवरी 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 63 Agenda item Request for the inclusion of a supplementary item in the agenda of the sixty-third session Need to examine the fundamental rights of the 23 million people of the Republic of China (Taiwan) to participate meaningfully in the activities of the United Nations specialized agencies A/63/194 2008-08-22. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ "Not even asking". The Economist. 2009-09-24. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ "Taiwan attends WHA as observer". United Press International. 18 May 2009.
- ↑ 35.0 35.1 35.2 35.3 35.4 35.5 35.6 35.7 35.8 "Yearbook of the United Nations". United Nations.
- ↑ Paul L. Montgomery (23 May 1992). "3 Ex-Yugoslav Republics Are Accepted into U.N." The New York Times. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 29 July 2012.
- ↑ Lewis, Paul (8 April 1993). "U.N. Compromise Lets Macedonia Be a Member". The New York Times.
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 "A Different Yugoslavia, 8 Years Later, Takes Its Seat at the U.N." The New York Times. 2 November 2000.
- ↑ Burns, John F. (28 April 1992). "Confirming Split, Last 2 Republics Proclaim a Small New Yugoslavia". The New York Times.
- ↑ "History of Serbia: The Break-up of SFR Yugoslavia (1991–1995)". Serbia Info. Archived from the original on 22 December 2007.
- ↑ "United Nations Security Council Resolution 757" (PDF). United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 अगस्त 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ "United Nations General Assembly Resolution A/RES/47/1" (PDF). United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 अगस्त 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ Sudetic, Chuck (24 September 1992). "U.N. Expulsion of Yugoslavia Breeds Defiance and Finger-Pointing". The New York Times.
- ↑ "Yugoslavia consigned to history". BBC News. 4 February 2003.
- ↑ "World Briefing – Europe: Serbia: Going Solo". The New York Times. 6 जून 2006.
- ↑ Schneider, Daniel B. (29 जून 2006). "World Briefing – Europe: Montenegro: U.N. Makes It Official". The New York Times.
- ↑ "IMF Members' Quotas and Voting Power, and IMF Board of Governors". International Monetary Fund.
- ↑ "World Bank Group Members". World Bank. Archived from the original on 2011-02-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (help) - ↑ "Kosovo independence not illegal, says UN court". BBC News. 22 July 2010.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 John R. Bolton (1 July 2000). "New Directions for the Chen Administration on Taiwanese Representation in the United Nations". China Affairs Quarterly. American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research. 1: 29.
- ↑ "United Nations General Assembly Resolution A/RES/48/258" (PDF). United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 सितंबर 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ Blum, Yehuda Zvi (1993). Eroding the United Nations Charter. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 0-7923-2069-7.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Gharib, Ali (20 December 2012). "U.N. Adds New Name: "State of Palestine"". The Daily Beast. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ↑ "Vatican City (Holy See)". World Statesmen.org.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 58 Resolution 314. Participation of the Holy See in the work of the United Nations A/RES/58/314 2004-07-16. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 29 Resolution 3237. Observer status for the Palestine Liberation Organization A/RES/3237(XXIX) 1974-11-22. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 43 Resolution 177. Question of Palestine A/RES/43/177 1988-12-15. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 66 Agenda item 116. Application of Palestine for admission to membership in the United Nations A/66/371 2011-09-23. Retrieved 2016-04-16.
- ↑ "Ban sends Palestinian application for UN membership to Security Council". United Nations. 23 September 2011.
- ↑ "General Conference admits Palestine as UNESCO Member State". United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. 31 अक्टूबर 2011.
- ↑ United Nations General Assembly Session 67 Resolution 19. Status of Palestine in the United Nations A/RES/67/19 2012-12-04. Retrieved 2016-04-24.
- ↑ "Palestinians win implicit U.N. recognition of sovereign state". Reuters. 29 November 2012. Retrieved 29 November 2012.
- ↑ "UN makes Palestine nonmember state". 3 News NZ. 30 November 2012. Archived from the original on 16 January 2013. Retrieved 19 February 2018.
- ↑ "Israel defies UN after vote on Palestine with plans for 3,000 new homes in the West Bank". The Independent. 1 December 2012.
- ↑ The Holy See, the Order of Malta and International Law Archived 2015-11-21 at the Wayback Machine, Bo J. Theutenberg, ISBN 91-974235-6-4
- ↑ "Malta Permanent Mission to the United Nations". Un.int. Retrieved 12 April 2016.
- ↑ "What is a Permanent Observer?". United Nations.
- ↑ Osmańczyk, Jan (2003). Mango, Anthony (ed.). Encyclopedia of the United Nations and International Agreements (3rd ed.). Routledge. ISBN 0-415-93920-8.
- ↑ McNeely, Connie L. (1995). Constructing the Nation-State: International Organization and Prescriptive Action. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 44–45. ISBN 978-0-313-29398-6.
- ↑ "Security Council Recommends Admission of Switzerland as Member of United Nations". United Nations. 24 July 2002.
- ↑ "About the EU at the UN – European Union Delegations". Europa. Archived from the original on 4 सितंबर 2006. Retrieved 22 सितंबर 2011.
- ↑ "Resolution adopted by the General Assembly: Participation of the European Union in the work of the United Nations" (PDF). United Nations. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 दिसंबर 2013. Retrieved 22 सितंबर 2011.
- ↑ "About the EU at the UN". Europa. Archived from the original on 12 फरवरी 2008. Retrieved 22 सितंबर 2011.
- ↑ "Non-Self-Governing Territories". United Nations.
- ↑ "Countries". World Health Organization.
- ↑ "Member States". United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization. Archived from the original on 8 जुलाई 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (help) - ↑ 77.0 77.1 "Organs Supplement", Repertory of Practice (PDF), UN, p. 10
- ↑ The World today (PDF), UN
- ↑ "Parties to the Convention and Observer States". United Nations.
- ↑ "Chronological lists of ratifications of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea". United Nations.
- ↑ "The World Today" (PDF). United Nations.
- ↑ "NZ PM rules out discussion on Cooks UN membership". Radio New Zealand. 2015-06-19. Retrieved 2016-04-16.
- ↑ "Niue to seek UN membership". Radio New Zealand. 2016-10-27. Retrieved 2017-07-08.
बाहरी कड़ी
[संपादन करीं]| विकिमीडिया कॉमंस पर संबंधित मीडिया Member states of the United Nations पर मौजूद बा। |