Hypéroside
| Hypéroside | |
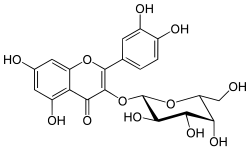
| |
| Structure de l'hypéroside. | |
| Identification | |
|---|---|
| Synonymes |
Hypérine |
| No CAS | |
| No ECHA | 100.006.892 |
| PubChem | 5281643 |
| Apparence | Poudre jaune |
| Propriétés chimiques | |
| Formule | C21H20O12 |
| Masse molaire[1] | 464,376 3 ± 0,021 8 g/mol C 54,31 %, H 4,34 %, O 41,34 %, |
| Composés apparentés | |
| Autres composés | |
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |
| modifier |
|
L’hypéroside est un composé organique de la famille des flavonols : un glycoside de la quercétine et plus précisément un 3-O-galactoside de la quercétine.
C'est un composé très répandu dans les plantes, notamment dans les feuilles et pétioles de Rheum rhaponticum, dans Geranium niveum, une plante de la médecine mexicaine, ou dans Taxillus kaempferi.
Références
[modifier | modifier le code]- Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- (en) Li Shiyou, Zhang Zhizhen, Cain Abigail, Wang Bo, Long Melissa & Taylor Josephine, 2005. Antifungal Activity of Camptothecin, Trifolin, and Hyperoside Isolated from Camptotheca acuminata. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53 (1), pages 32–7, DOI 10.1021/jf0484780, .
- (en) Van Der Watt Elmarie & Pretorius Johan C., 2001. Purification and identification of active antibacterial components in Carpobrotus edulis L. Journal of Ethnopharmacology. 76 (1), pages 87–91, DOI 10.1016/S0378-8741(01)00197-0, .
- (en) Calzada F., Cerda-García-Rojas C.M., Meckes M., Cedillo-Rivera R., Bye R. & Mata R., 1999. Geranins a and B, new antiprotozoal A-type proanthocyanidins from Geranium niveum. Journal of Natural Products. 62 (5), pages 705–709, DOI 10.1021/np980467b, .
- (en) Konishi T., Nishio T., Kiyosawa S., Fujiwara Y., Konoshima T. & Yakugaku Zasshi, 1996. The constituents of Taxillus kaempferi and the host, Pinus thunbergii. I. Catechins and flavones of Taxillus kaempferi. February 1996, volume 116, issue 2, pages 148-157 (article en japonais).