लिपियों की सूची
| यह सम्पूर्ण पृष्ठ या इसके कुछ अनुभाग हिन्दी के अतिरिक्त अन्य भाषा(ओं) में भी लिखे गए हैं। आप इनका करके विकिपीडिया की सहायता कर सकते हैं। |
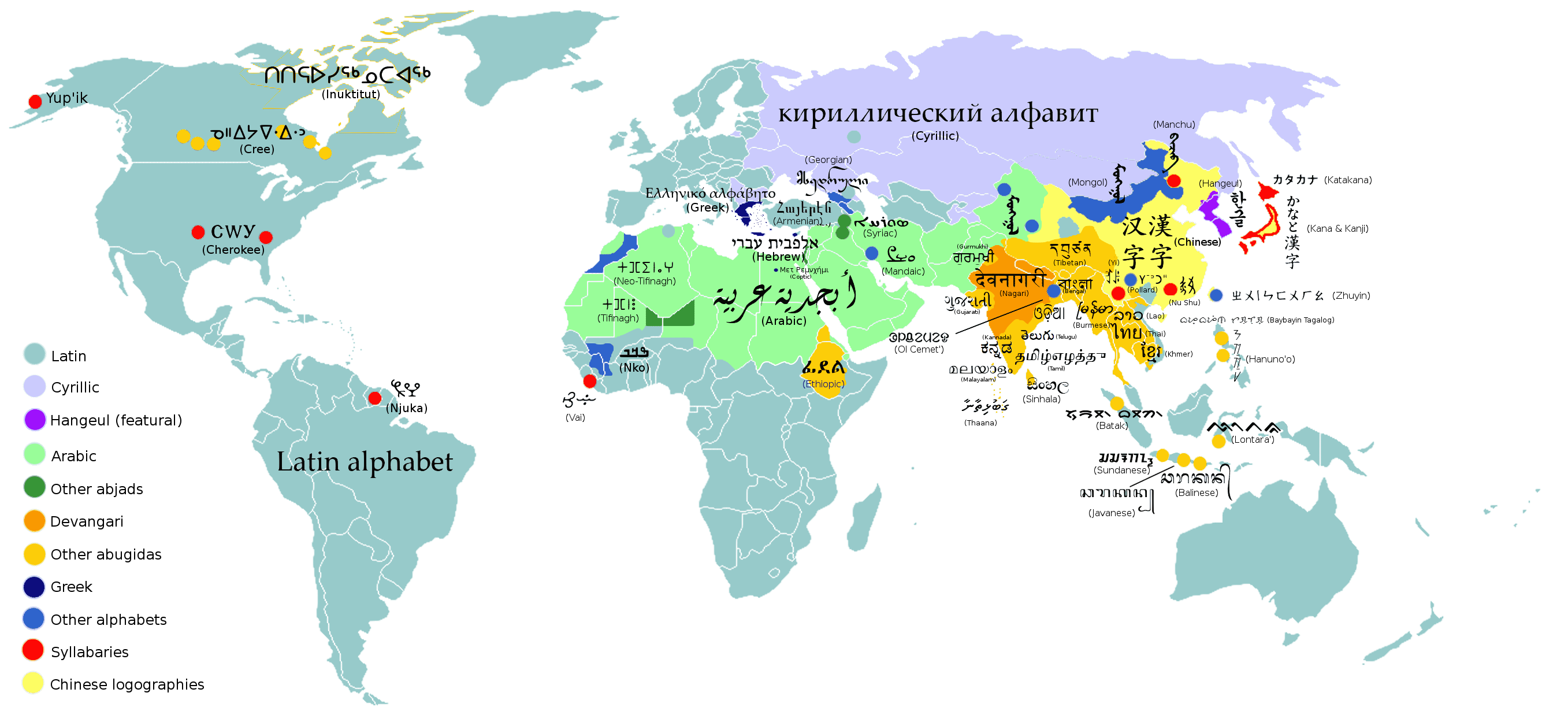
यहाँ विश्व की 'लेखन पद्धतियों' या लिपियों की वर्गीकृत सूची दी गई है। यह वर्गीकरण लिपियों के किसी विशेष गुण के आधार पर किया गया है जो उनकोअन्य लिपियों से अलग करता है।
पहले लिपि का नाम दिया गया है, इसके बाद उस लिपि में लिखी जाने वाली भाषाओं के नाम कोष्टक में दिए गए हैं।
चित्रात्मक/भावचित्रात्मक लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]- Aztec – Nahuatl – Although some proper nouns have phonetic components.[1]
- Mixtec – Mixtec
- Dongba – Naxi – Although this is often supplemented with syllabic Geba script.
- Ersu Shābā – Ersu
- Míkmaq hieroglyphic writing – Míkmaq – Does have phonetic components, however.
- Nsibidi – Ekoi, Efik/Ibibio, Igbo
- Testerian – used for missionary work in Mexico
- Other Mesoamerican writing systems with the exception of Maya Hieroglyphs.
There are also symbol systems used to represent things other than language, or to represent constructed languages. Some of these are
- Blissymbols – A constructed ideographic script used primarily in Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC).
- iConji – A constructed ideographic script used primarily in social networking
- Isotype (picture language)
- Sona language
- A wide variety of notations
Linear B and Asemic writing also incorporate ideograms.
शब्द-चिह्न लेखनपद्धति
[संपादित करें]व्यंजन-आधारित शब्द-चिह्नात्मक लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]- Hieroglyphic, Hieratic, and Demotic – writing systems of Ancient Egypt
अक्षरधारित शब्दचिह्नात्मक लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]- Anatolian hieroglyphs – Luwian
- Cuneiform – Sumerian, Akkadian, other Semitic languages, Elamite, Hittite, Luwian, Hurrian, and Urartian
- Chinese characters (Hanzi) – Chinese, Japanese (called Kanji), Korean (called Hanja), Vietnamese (called Han tu, obsolete)
- Jurchen script – Jurchen
- Khitan large script – Khitan
- Tangut script – Tangut
- Zhuang script – Zhuang
- Chữ Nôm – Vietnamese (for vernacular Vietnamese, now obsolete)
- Eghap (or Bagam) script
- Mayan – Chorti, Yucatec, and other Classic Maya languages
- Yi (classical) – various Yi/Lolo languages
- Shui script – Shui language
अक्षरात्मक
[संपादित करें]In a syllabary, graphemes represent syllables or moras. (Note that the 19th century term syllabics usually referred to abugidas rather than true syllabaries.)
- Afaka – Ndyuka
- Alaska script – Central Yup'ik
- Cherokee – Cherokee
- Cypriot – Mycenean Greek
- Geba – Naxi
- Kana – Japanese**Hiragana –
- Kikakui – Mende
- Kpelle – Kpelle
- Linear B – Mycenean Greek
- Nü Shu – Chinese
- Vai – Vai
- Woleaian – Woleaian (a likely syllabary)
- Yi (modern) – various Yi/Lolo languages
अर्ध-अक्षरात्मक लिपियाँ (अंशतः अक्षरात्मक तथा अंशतः वर्णात्मक
[संपादित करें]- Old Persian Cuneiform – Old Persian
- Zhuyin fuhao – phonetic script for Chinese languages, and principal script for several Formosan languages.
- Eskayan – Bohol, Philippines (a syllabary apparently based on an alphabet; some alphabetic characteristics remain)
- Bamum script – Bamum (a defective syllabary, with alphabetic principles used to fill the gaps)
खण्डयुक्त लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]अबजाद (Abjads)
[संपादित करें]An abjad is a segmental script containing symbols for consonants only, or where vowels are optionally written with diacritics ("pointing") or only written word-initially.
- Aramaic
- Arabic – Arabic, Azeri, Punjabi, Baluchi, Kashmiri, Pashto, Persian, Kurdish (vowels obligatory), Sindhi, Uighur (vowels obligatory), Urdu, and the languages of many other peoples of the Near East
- Hebrew Square Script – Hebrew, Yiddish, and other Jewish languages
- Jawi – Arabic, Malay
- Manichaean script
- Nabataean – the Nabataeans of Petra
- Pahlavi script – Middle Persian
- Phoenician – Phoenician and other Canaanite languages
- Proto-Canaanite
- Sabaean
- South Arabian – Sabaic, Qatabanic, Himyaritic, and Hadhramautic
- Sogdian
- Samaritan (Old Hebrew) – Aramaic, Arabic, and Hebrew
- Syriac – Syriac
- Tifinagh – Tuareg
- Ugaritic – Ugaritic, Hurrian
शुद्ध वर्णात्मक लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]A true alphabet contains separate letters (not diacritic marks) for both consonants and vowels.
रैखिक गैरलक्षणात्मक वर्ण लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]
Linear alphabets are composed of lines on a surface, such as ink on paper.
- Uyghur Arabic alphabet (Uyghur Ereb Yéziqi) – Avestan
- Armenian – Armenian
- Avestan alphabet – Avestan
- Beitha Kukju – Albanian
- Borama – Somali
- Caucasian Albanian alphabet – Old Udi language
- Coptic – Egyptian
- Cyrillic – Eastern Slavic languages (Belarusian, Russian, Ukrainian), eastern South Slavic languages (Bulgarian, Macedonian, Serbian), the other languages of Russia, Kazakh language, Kyrgyz language, Tajik language, Mongolian language. Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan are changing to the Latin alphabet but still have considerable use of Cyrillic. See Languages using Cyrillic.
- Eclectic Shorthand
- Elbasan – Albanian
- Fraser – Lisu
- Gabelsberger shorthand
- Georgian – Georgian and other Kartvelian languages
- Glagolitic – Old Church Slavonic
- Gothic – Gothic
- Greek – Greek
- International Phonetic Alphabet
- Kaddare – Somali
- Latin aka Roman – originally Latin language; most current western and central European languages, Turkic languages, sub-Saharan African languages, indigenous languages of the Americas, languages of maritime Southeast Asia and languages of Oceania use developments of it. Languages using a non-Latin writing system are generally also equipped with Romanization for transliteration or secondary use.
- Manchu – Manchu
- Mandaic – Mandaic dialect of Aramaic
- Mongolian – Mongolian
- Neo-Tifinagh – Tamazight
- N'Ko – Maninka language, Bambara, Dyula language
- Ogham (Irish pronunciation: [oːm]) – Gaelic, Britannic, Pictish
- Old Hungarian (in Hungarian magyar rovásírás or székely-magyar rovásírás) – Hungarian
- Old Italic – a family of connected alphabets for the Etruscan, Oscan, Umbrian, Messapian, South Picene, Raetic, Venetic, Lepontic, Camunic languages
- Old Permic (also called Abur) – Komi
- Old Turkic – Turkic
- Old Uyghur alphabet – Uyghur
- Osmanya – Somali
- Runic alphabet – Germanic languages
- Ol Cemet' – Santali
- Tai Lue – Lue
- Vah – Bassa
- Zaghawa – Zaghawa
लक्षणात्मक रैखिक वर्णात्मक लिपियाँ (Featural linear alphabets)
[संपादित करें]A featural script has elements that indicate the components of articulation, such as bilabial consonants, fricatives, or back vowels. Scripts differ in how many features they indicate.
- Gregg Shorthand
- Hangul – Korean
- Shavian alphabet
- Tengwar (a fictional script)
- Visible Speech (a phonetic script)
- Stokoe notation for American Sign Language
- SignWriting for sign languages
दिग्दर्शी वर्णात्मक (Manual alphabets)
[संपादित करें]Manual alphabets are frequently found as parts of sign languages. They are not used for writing per se, but for spelling out words while signing.
- American manual alphabet (used with slight modification in Hong Kong, Malaysia, Paraguay, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand)
- British manual alphabet (used in some of the Commonwealth of Nations, such as Australia and New Zealand)
- Catalonian manual alphabet
- Chilean manual alphabet
- Chinese manual alphabet
- Dutch manual alphabet
- Ethiopian manual alphabet (an abugida)
- French manual alphabet
- Greek manual alphabet
- Icelandic manual alphabet (also used in Denmark)
- Indian manual alphabet (a true alphabet?; used in Devanagari and Gujarati areas)
- International manual alphabet (used in Germany, Austria, Norway, Finland)
- Iranian manual alphabet (an abjad; also used in Egypt)
- Israeli manual alphabet (an abjad)
- Italian manual alphabet
- Korean manual alphabet
- Latin American manual alphabets
- Polish manual alphabet
- Portuguese manual alphabet
- Romanian manual alphabet
- Russian manual alphabet (also used in Bulgaria and ex-Soviet states)
- Spanish manual alphabet (Madrid)
- Swedish manual alphabet
- Yugoslav manual alphabet
अन्य अरैखिक वर्ण (Other non-linear alphabets)
[संपादित करें]These are other alphabets composed of something other than lines on a surface.
- Braille (Unified) – an embossed alphabet for the visually impaired, used with some extra letters to transcribe the Latin, Cyrillic, Greek, Hebrew, and Arabic alphabets, as well as Chinese
- Braille (Korean)
- Braille (American) (defunct)
- New York Point – a defunct alternative to Braille
- International maritime signal flags (both alphabetic and ideographic)
- Morse code (International) – a trinary code of dashes, dots, and silence, whether transmitted by electricity, light, or sound) representing characters in the Latin alphabet.
- American Morse code (defunct)
- Optical telegraphy (defunct)
- Flag semaphore – (made by moving hand-held flags)
आबूगीदा (Abugidas)
[संपादित करें]इन्हें वर्णाक्षरी (अल्फासिलैबरी) भी कहते हैं। ये 'खण्डात्मक' (segmental) लिपियाँ है जिनमें स्वर चिह्नों को दर्शाने के लिए व्यंजन पर कोई डायाक्रिटिकल चिह्न लगाया जाता है या कोई अन्य परिवर्तन/परिवर्धन कर दिया जाता है। भारत तथा दक्षिण-पूर्व एशिया की प्रायः सभी लिपियाँ इसी श्रेणी में आती हैं। ये सभी ऐतिहासिक रूप से ब्राह्मी परिवार की हैं।
ब्राह्मी परिवार की आबूगीदा लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]
- Anga Script – Angika
- Ahom
- Assamese – Assamese/Assamiya/Ôxômiya
- ब्राह्मी लिपि – प्रकृत, संस्कृत
- Balinese
- Batak – Toba and other Batak languages
- Baybayin – Ilokano, Kapampangan, Pangasinan, Tagalog, Bikol languages, Visayan languages, and possibly other Philippine languages
- बांग्ला लिपि – बांग्ला भाषा, मैथिली भाषा
- Buhid
- Burmese – Burmese, Karen languages, Mon, and Shan
- Cham
- Dehong – Dehong Dai
- देवनागरी – हिन्दी, सम्स्कृत, मराठी, नेपाली, तथा उत्तरी भारत एवं नेपाल की अनेकों भाषाएँ
- Gujarāti – Gujarāti, Kachchi
- Gurmukhi script – Punjabi
- Hanuno’o
- Javanese
- Kaganga – Rejang
- Kaithi
- Kannada – Kannada, Tulu
- Kawi
- Khmer
- Lao
- Limbu
- Lontara’ – Buginese, Makassar, and Mandar
- Malayalam
- Mithilākshara {syn. Vaidehī lipi / Tirahutā / Tirhutā } Used to write Maithili
- Modi – Marathi
- Nepal – Nepal Bhasa, Sanskrit
- Oriya
- Phags-pa – Mongolian, Chinese, and other languages of the Yuan Dynasty Mongol Empire
- Ranjana – Nepal Bhasa, Sanskrit
- Śāradā
- Siddham used to write Sanskrit
- Sinhala
- Sourashtra
- Soyombo
- Sundanese
- Syloti Nagri – Sylheti
- Tagbanwa – Languages of Palawan
- Tai Dam
- Tai Tham – Khün, and Northern Thai
- Tamil
- Telugu
- Thai
- Tibetan
- Tirahutā / Tirhutā {syn. Vaidehī lipi / Mithilākshara } used to write Maithili
- Tocharian
- Varang Kshiti – Ho
अन्य आबूगीदा लिपियाँ
[संपादित करें]- Canadian Aboriginal syllabics – Cree syllabics (for Cree), Inuktitut syllabics (for Inuktitut), and other variants for Ojibwe, Carrier, Blackfoot, and other languages of Canada
- Ethiopic – Amharic, Ge’ez, Oromo, Tigrigna
- Kharoṣṭhī – Gandhari, Sanskrit
- Mandombe
- Meroitic – Meroë
- Pitman Shorthand
- Pollard script – Miao
- Sorang Sompeng – Sora
- Thaana – Dhivehi
- Thomas Natural Shorthand
अन्तिम व्यंजन-डायाक्रिटिक अबुगिडा (Final consonant-diacritic abugidas)
[संपादित करें]स्वरधारित आबूगीदा लिपियाँ (Vowel-based abugidas)
[संपादित करें]लिपियाँ जिन्हें अभी तक समझा नहीं जा सका है।
[संपादित करें]- Byblos syllabary – the city of Byblos
- Isthmian (apparently logosyllabic)
- Indus – Indus Valley Civilization
- Quipu – Inca Empire (probably numerical only)
- Khitan small script – Khitan
- Cretan hieroglyphs
- Linear A (a syllabary) – Minoan
- Mixtec – Mixtec (perhaps pictographic)
- Olmec – Olmec civilization (possibly the oldest Mesoamerican script)
- Phaistos Disc (a unique text, very possibly not writing)
- Proto-Elamite – Elam (nearly as old as Sumerian)
- Rongorongo – Rapa Nui (perhaps a syllabary)
- Proto-Sinaitic (likely an abjad)
- Zapotec – Zapotec (another old Mesoamerican script)
- Banpo symbols – Yangshao culture (perhaps proto-writing)
- Jiahu symbols – Peiligang culture (perhaps proto-writing)
पाण्डुलियाँ जिन्हें अभी तक समझा नहीं गया है
[संपादित करें]अन्य
[संपादित करें]Asemic writing is generally meaningless, though it sometimes contains ideograms or pictograms.
ध्वन्यात्मक वर्णमाला वाली लियियाँ (Phonetic alphabets)
[संपादित करें]This section lists alphabets used to transcribe phonetic or phonemic sound; not to be confused with spelling alphabets like the ICAO spelling alphabet.
- International Phonetic Alphabet
- Deseret alphabet
- Unifon
- Americanist phonetic notation
- Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
- Shavian alphabet
विशिष्ट वर्णमालाएँ
[संपादित करें]Alphabets may exist in forms other than visible symbols on a surface. Some of these are:
Tactile alphabets
[संपादित करें]Manual alphabets
[संपादित करें]For example:
Long-Distance Signaling
[संपादित करें]Alternative alphabets
[संपादित करें]Fictional writing systems
[संपादित करें]- Ath (alphabet)
- Aurebesh
- Cirth
- D'ni
- Goa'uld
- Hymmnos
- Klingon
- On Beyond Zebra!
- Quenya
- Sarati
- Sindarin
- Tengwar
- Unown
पशुओं द्वारा उपयोग के लिए
[संपादित करें]- युर्किश (Yurkish) लिपि मानवेतर प्राइमेट्स के साथ 'बातचीत' करने के लिए लेक्सिग्रामों (lexigrams) का प्रयोग करती है।
बाहरी कड़ियाँ
[संपादित करें]- Omniglot: a guide to writing systems
- Ancient Scripts: Home:(Site with some introduction to different writing systems and group them into origins/types/families/regions/timeline/A to Z)
सन्दर्भ
[संपादित करें]- ↑ Smith, Mike (1997). The Aztecs. Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishing. ISBN 0-631-23015-7.