シガトキシン
| Ciguatoxin 1B | |
|---|---|

| |
別称 Ciguatoxin, ciguatoxin 1 | |
| 識別情報 | |
| CAS登録番号 | 11050-21-8 |
| PubChem | 5311333 |
| 日化辞番号 | J1.866.175F |
| 特性 | |
| 化学式 | C60H86O19 |
| モル質量 | 1111.31 g mol−1 |
| 危険性 | |
| 半数致死量 LD50 | 11 mg/kg(ラット、静注) 530 mg/kg(マウス、経口) 250 ng/kg(マウス、腹腔) |
| 出典 | |
| LD50; ラット (i.v.),[1] マウス (p.o.,[2] i.p.[3]) [4] | |
| 特記なき場合、データは常温 (25 °C)・常圧 (100 kPa) におけるものである。 | |
シガトキシン (ciguatoxin) はシガテラ食中毒の原因物質のひとつ。非常に強い神経毒。ある種の藻類(有毒渦鞭毛藻)がつくり、魚類に蓄積される[5]。ポリケチド経路によって生合成され、中員環を含む多数のエーテル環が連結した特異な構造を持つ。シガトキシン (CTX) には数多くの類縁体が存在するが、一般的にシガトキシンとはCTX1Bを指す。
毒性
[編集]毒性は、ナトリウムチャネルのサイト4に結合し、フグ毒テトロドトキシンとは逆にナトリウム透過性を高めることにより発現すると推測されている。脱分極の結果、まひ、心収縮、聴覚や温度感覚の変化が起こる。シガトキシンは血液脳関門を通過しないため、末梢神経系で作用する。
主な症状は、ドライアイスセンセーション(温度感覚の異常)、掻痒、四肢の痛み、筋肉痛、関節痛、下痢、嘔吐、頭痛、めまい、脱力、排尿障害などである[6]。
毒素汚染食品を簡単に検出するためのに、「2種のモノクローナル抗体を組み合わせ、M環部に水酸基を有するシガトキシン類を特異的に検出できる測定キット」が科学技術振興事業団、東北大学らの研究グループにより開発された[7]。
単離と命名
[編集]1967年にハワイ大学のScheuerらによって単離・命名され[8]、1989年に東北大学の安元健らによって構造決定された[9]。
名前は毒を持つ巻貝シガ (Cigua, Cittarium pica) に由来する。なお、一部の赤痢菌が産生するシガトキシン(Shigatoxin、志賀毒素)については、ベロ毒素(=志賀毒素)の項を参照。Shigatoxinと、本項のシガトキシン(Ciguatoxin)は全く別の物質である。
全合成
[編集]2001年に東北大学の平間正博および上原久俊、丸山潤美らを中心としたグループにより、シガトキシン (CTX3C) の全合成が世界で初めて報告された。グラブス触媒を用いたオレフィンメタセシスによる閉環反応を鍵反応とし、13個の連結したエーテル環構造を効率的に合成する手法を確立し、以後の天然物合成における可能性を広げた[10][11][12]。
類縁体
[編集]| 名称 | 構造式 | CAS | PubChem | 分子式 | 備考 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

|
11050-21-8 | CID 5311333 - PubChem | C60H86O19 | |
|

|
142185-85-1 | CID 6441260 - PubChem | C60H86O18 | CTX3のジアステレオマー(52位エピマー) |
|

|
139341-09-6 | CID 6444399 - PubChem | C60H86O18 | CTX2のジアステレオマー(52位エピマー) |
|
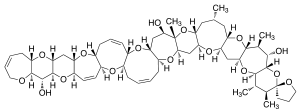
|
148471-85-6 | CID 6442245 - PubChem | C57H82O16 | シガトキシンの中では極性が低く、毒性も相対的に劣っている |
|

|
C57H82O17 | |||
|

|
C60H84O16[13] | CTX4Bのジアステレオマー | ||
|

|
123676-76-6 66231-73-0 |
CID 6450530 - PubChem | C60H84O16 | CTX4Aのジアステレオマー[14] |
|
136252-00-1 |
脚注
[編集]- ^ Kosaki, T. I.; Anderson, H. H. (1968). “Marine toxins from the Pacific—IV Pharmacology of ciguatoxin(s)”. Toxicon 6 (1): 55-56, IN5-IN6, 57-58. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(68)90066-4.
- ^ Ogura, Y.; Nara, J.; Yoshida, T. (1968). “Comparative pharmacological actions of ciguatoxin and tetrodotoxin, a preliminary account”. Toxicon 6 (2): 131-140. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(68)90032-9.
- ^ Lewis, R. J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M. A.; Norton, R. S.; MacLeod, J. K.; Sheil, M. M. (1991). “Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae)”. Toxicon 29 (9): 1115-1127. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(91)90209-A.
- ^ Chemcas (2010年10月23日). “MSDS Ciguatoxin CAS 11050-21-8 MSDS * Ciguatoxin 1 * Ciguatoxin CTX 1 * CTX 1”. 2010年10月23日閲覧。
- ^ 鈴木勉、田中真知『学研雑学百科 毒学教室 毒のしくみから世界の毒事件簿まで 毒のすべてをわかりやすく解説』株式会社学研マーティング、2011年、46ページ、ISBN 978-4-05-404832-4
- ^ 厚生労働省. “自然毒のリスクプロファイル:魚類:シガテラ毒”. 2010年10月22日閲覧。
- ^ j-platpat (2006年). “シガトキシン類を認識するモノクローナル抗体、およびそれを用いるシガトキシン類検出キット”. 2022年3月10日閲覧。
- ^ Nukina, M.; Koyanagi, L. M.; Scheuer, P. J. (1984). “Two interchangeable forms of ciguatoxin”. Toxicon 22 (2): 169-176. doi:10.1016/0041-0101(84)90017-5. PMID 6203187.
- ^ Murata, M; Legrand, A. M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Yasumoto, T. (1989). “Structures of ciguatoxin and its congener”. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 111 (24): 8929-8931. doi:10.1021/ja00206a032.
- ^ Hirama, M.; Oishi, T.; Uehara, H.; Inoue, M.; Maruyama, M.; Oguri, H.; Satake, M. (2001). “Total Synthesis of Ciguatoxin CTX3C”. Science 294 (5848): 1904-1907. doi:10.1126/science.1065757. PMID 11729311.
- ^ 総説:Hirama, M. (2005). “Total synthesis of ciguatoxin CTX3C: a venture into the problems of ciguatera seafood poisoning”. Chem. Rec. 5 (4): 240-250. doi:10.1002/tcr.20049. PMID 16059875.
- ^ 大石徹「超微量海産神経毒シガトキシンCTX3Cの全合成」『有機合成化学協会誌』第61巻第6号、有機合成化学協会、2003年、562-571頁、doi:10.5059/yukigoseikyokaishi.61.562。
- ^ Oguri, H. (2007). “Bioorganic Studies Utilizing Rationally Designed Synthetic Molecules: Absolute Configuration of Ciguatoxin and Development of Immunoassay Systems”. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jap. 80 (10): 1870-1883. doi:10.1246/bcsj.80.1870.
- ^ Luis M. Botana (2000). Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection. NY: Marcel Dekker. ISBN 978-0824789565