ブルーヘッド
| ブルーヘッド | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 保全状況評価[1] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LEAST CONCERN (IUCN Red List Ver.3.1 (2001)) 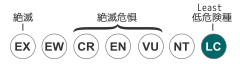
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 分類 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 学名 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thalassoma bifasciatum (Bloch, 1791) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| シノニム | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 英名 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| bluehead bluehead wrasse Doubleband wrasse |

ブルーヘッド(Bluehead、またはDoubleband wrasse[2],学名:Thalassoma bifasciatum)はスズキ目ベラ科ニシキベラ属の海水魚。西大西洋の熱帯域に分布し、サンゴ礁で大きな群れを作る掃除魚である。小型であり、寿命は2年程度と短い。観賞魚としてアクアリウムで飼育されるが、遊泳力が高いため広めの水槽が必要である。
分布と生息地
[編集]フロリダからベネズエラまで、主にカリブ海とメキシコ湾南東部の西大西洋沿岸に分布する[1]。水深3 - 30mのサンゴ礁、湾、藻場に生息する。幼魚は海藻の周辺に多い[2]。
形態
[編集]
全長は最大25cmだが、通常は10 - 15cm程度。体は細長く、雄の成魚(TP)は頭部が青色で体が緑色を帯びており、その間に黒く縁どられた白色または薄い青色帯がある。雌や幼魚(IP)は背側が黄色、腹側は白色で、ある程度大きい個体は暗色縦線が入り、頬は赤い[2][3]。瞬時に体色や模様を変えることができる。8cm程度でTPオスとなる[4]。
生態
[編集]食事
[編集]動物プランクトン、軟体動物、エビやオキアミなど小型の甲殻類、蠕虫、運動性無脊椎動物、魚卵だけでなく、他の魚の外部寄生虫も捕食する[5] 。IPオスは主に浮遊している動物プランクトンを流れに乗って捕食し、メスとIPオスは日中に捕食を行う[6]。
捕食者と寄生虫
[編集]分布域のサンゴ礁では一般的な掃除魚だが、ウツボやハタなどの肉食魚には捕食される危険性があるため行わない。代わりにハゼが肉食魚の掃除を行っている[7]。ハタやエイ、ヘラヤガラなどに捕食される[1][8]。
本種の寄生虫として、ミクソゾアである Kudoa ovivora のメスの卵巣への寄生が知られている。寄生された卵は無精卵で、寄生されていない卵より大きく、物質をより多く含む。これは寄生虫により母体の栄養が卵に行き渡るようになり、母親の体力が低下することを示している[9]。寄生された個体はより早く性転換することが明らかになっている[10]。
保全
[編集]大西洋北西部に広く分布しており、プエルトリコ、ヴァージン諸島、アンティル諸島付近のサンゴ礁では特に個体数が多い。国際自然保護連合によって低危険種とされているが、生息地への依存性が強いため、サンゴ礁の破壊によって大幅に数を減らす可能性もある。食用にはされず鮮やかな体色のためアクアリウムで飼育されるが、このための捕獲は本種に影響を与えてはいない[1]。
生態
[編集]本種は雌性先熟の雌雄同体で、メスは性転換してTPオスとなる場合がある。
社会システム
[編集]
オスの中には特定の社会システムがあり、成熟したTPオスは攻撃的で序列が高く、若いIPオスはより大きな集団の中でチャンスが得られると交尾する。体色の変化は感情や状態を示し、TPオスがIPオスを追いかけるとき、体色はメタリックな緑色に変わり、メスに求愛するときはピンクや灰色になり、鰭には黒い円が現れる[11]。
性転換
[編集]IPの雌雄はTPオスになる可能性があり、変化は8日程度と比較的早く行われる。しかし一旦変化すると戻ることはできない。群れからTPオスを取り除く実験では、多くのIPメスがTPオスになり、攻撃性が増して体色も変化した[12]。IPオスはTPオスよりも大きな精巣を持つ。これにより、現在はTPオスに群れ内での受精の機会を奪われているが、将来TP化した時のために多くの精子を生産できる[13]。IPオスも集団産卵の際には受精を行うことができる。集団産卵の際、IPオスは20 - 50尾の群れを作り、メスはこれらの群れを訪れ産卵を行う。IPオスは受精確率を上げるためメスの隣に位置し、大きな精巣を利用し多数の精子を放出する。これらの競争は多くの種で見られる。
性転換に関する研究
[編集]本種と同属種のサドルラスは、性転換を生理学的、神経生物学的に理解する重要なモデルとなっている。性転換は群れで最大の個体をメスにすることで誘導することができる。実験により、性転換では生殖腺における主要なステロイドホルモン(エストラジオールと11-ケトテストステロン)とステロイドホルモン合成酵素の減少に伴う生殖腺の変化が起こると分かった。性転換した個体はモノアミン神経伝達物質であるセロトニン、ドーパミン、ノルアドレナリンの脳内濃度に大きな変化を示す。
雌性先熟の為、IPオス、IPメス、TPオス全てに繁殖能力がある。小さなサンゴ礁にはIPオスよりもTPオスの方が多く、少数のメスを守っている。大きなサンゴ礁では、IPとTPのオスの割合が同じになり、IPオスはTPオスに比べて攻撃性が低いため、交尾する可能性が高まる[4][12][14]。小さなサンゴ礁からTPオスを除去することによって、大型のメスに性転換を誘導することができる。性腺刺激ホルモン放出ホルモン(GnRH)ニューロンは、視床下部の表現型や、性転換を誘導するアンドロゲンの移動によって異なる。野外条件下では性転換が非常に速く、TPオスが除去された後、数分から数時間以内にオスに典型的な行動が観察される。行動的性転換は、群れ内で優位になる前に卵巣を切除したメスでも起こる。行動的性転換は、アルギニンバソトシン(AVT)と呼ばれる神経ペプチドホルモンの発現の増加と関連しており、これらの増加は、性転換するメスに生殖腺があるかどうかに関係なく発生する。AVTの注射はTPオスの性的および攻撃的な行動を誘発することができ、フルオキセチンの注射はTPオスの攻撃的な行動を軽減することができる。
配偶システム
[編集]大型のTPオスは、メスが毎日移動する繁殖地を守る。繁殖地を選択する際の各性別の役割を推定する研究が行われた。すべてのTPオスまたはすべてのメスを局所的に隔離した個体群と入れ替え、その結果生じる繁殖地の使用状況を観察した。オスを交換した後も、配偶システムは影響を受けなかった。メスが交換されると、古い繁殖地の半分は使われなくなり、同じ数の新しい繁殖地が使用されるようになり、1年以上使用され続けた。元々TPオスが古い繁殖地で防御を続けていたにもかかわらずこのような結果になった。これは繁殖地の選択においてはメスが重要で、オスがメスの好みに反応することを示している[15]。
本種は明確な縄張りを持たず、群れは自由に移動する。メスは通常元の産卵場所から離れず、オスは去ってしまうことが知られている。メスが留まる理由として、メスがその場所に最も慣れていることや、捕食者の脅威を避けるためなどが考えられる[6]。アメリカ領ヴァージン諸島のセント・クロイ島にある大きな直線状の堡礁では、前側近くの単一の場所に非常に大きな交配集団が毎日形成されている。タグ付けの研究によると、前側全体に散らばる特定の餌群に忠実で、1.5 km以上離れた産卵場に移動する傾向があることが示された。前側の他の場所では交尾が行われているようには見えない。移動に費やされる時間には大きな差があるにもかかわらず、交配集団と異なる場所に生息するメスの間で繁殖力や産卵の頻度には大きな差は無い。高い成長率はその場所における摂食率が高いことを示しており、食物摂取が長い移動のコストを上回る可能性があることを示唆している[16]。
脚注
[編集]- ^ a b c d Shea, S.; Liu, M.; Sadovy, Y. (2010). “Thalassoma bifasciatum”. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T187652A8590861. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-4.RLTS.T187652A8590861.en 02 January 2024閲覧。.
- ^ a b c Rudie H Kuiter (2015). Labridae Fishes: Wrasses. Reef Builders Inc. and Aquatic photographics
- ^ Froese, Rainer. “Thalassoma bifasciatum”. FishBase. 02 January 2024閲覧。
- ^ a b Warner, R. R.; Swearer, S. E. (October 1991). “Social Control of Sex Change in the Bluehead Wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum (Pisces: Labridae)”. The Biological Bulletin 181 (2): 199–204. doi:10.2307/1542090. JSTOR 1542090. PMID 29304633.
- ^ The Online Guide to the Animals of Trinidad and Tobago
- ^ a b DeLoach, Ned; Humann, Paul (1999). Reef fish behavior: Florida, Caribbean, Bahamas. Jacksonville, FL: New World Publications
- ^ Darcy, George H.; Maisel, Elizabeth; Ogden, John C. (June 1974). “Cleaning Preferences of the Gobies Gobiosoma evelynae and G. prochilos and the Juvenile Wrasse Thalassoma bifasciatum”. Copeia 1974 (2): 375–9. doi:10.2307/1442531. JSTOR 1442531.
- ^ Feddern, Henry A (December 1965). “The Spawning, Growth, and General Behavior of the Bluehead Wrasse, Thalassoma Bifasciatum”. Bulletin of Marine Science 15 (4): 896–941.
- ^ Swearer, Stephen E.; Robertson, D. Ross (April 1999). “Life History, Pathology, and Description of Kudoa ovivora n. sp. (Myxozoa, Myxosporea): An Ovarian Parasite of Caribbean Labroid Fishes”. The Journal of Parasitology 85 (2): 337–53. doi:10.2307/3285645. JSTOR 3285645. PMID 10219318.
- ^ Schärer, Lukas; Vizoso, Dita B. (2003). “Earlier sex change in infected individuals of the protogynous reef fish Thalassoma bifasciatum”. Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology 55 (2): 137–43. doi:10.1007/s00265-003-0694-0.
- ^ Dawkins, M.S.; Guilford, T. (1993). “Colour and pattern in relation to sexual and aggressive behaviour in the bluehead wrasse Thalassoma bifasciatum”. Behavioural Processes 30 (3): 245–51. doi:10.1016/0376-6357(93)90136-F. PMID 24896948.
- ^ a b Ford, D; Miranda, J.; Godwin, J.; Semsar, K.; Grober, M. (1999). “Sex Change in the Bluehead Wrasse: Temporal Concordance of Changes in Brain and Behavior”. Arizona State University Sixth Annual Undergraduate Research Poster Symposium.
- ^ Piper, Ross (2007). Extraordinary Animals: An Encyclopedia of Curious and Unusual Animals. Greenwood Press. ISBN 9780313339226
- ^ Godwin, J; Sawby, R; Warner, RR; Crews, D; Grober, MS (2000). “Hypothalamic arginine vasotocin mRNA abundance variation across sexes and with sex change in a coral reef fish”. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 55 (2): 77–84. doi:10.1159/000006643. PMID 10838478.
- ^ Warner, Robert R. (1995). “Large mating aggregations and daily long-distance spawning migrations in the bluehead wrasse, Thalassoma bifasciatum”. Environmental Biology of Fishes 44 (4): 337–45. doi:10.1007/BF00008248.
- ^ Warner, Robert R. (1990). “Male versus female influences on mating-site determination in a coral reef fish”. Animal Behaviour 39 (3): 540–8. doi:10.1016/S0003-3472(05)80420-8.