맥박압
| Pulse pressure | |
|---|---|
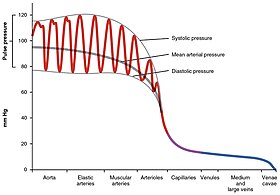 다양한 동맥과 정맥의 맥압 변화(pulse pressure variation, PPV) |
맥박압[1](pulse pressure, 맥압)은 수축기(systole) 혈압과 확장기(diastole) 혈압의 차이이다.[2] 수은주 밀리미터(mmHg) 단위로 측정된다. 이는 심장이 수축할 때마다 생성되는 힘을 나타낸다. 건강한 맥압은 약 40 mmHg이다.[2][3] 맥압이 지속적으로 60 mmHg 이상이면 질병과 관련될 가능성이 높으며, 맥압이 50 mmHg 이상이면 심혈관 질환의 위험이 높아진다.[2][4] 맥압이 수축기 혈압의 25% 미만이면 낮은 것으로 간주된다. (예를 들어 수축기 혈압이 120 mmHg인 경우 30 mmHg는 120의 25%이므로 30 mmHg 미만이면 맥압이 낮은 것으로 간주된다.)[3] 매우 낮은 맥압은 울혈성 심부전과 같은 장애의 증상일 수 있다.[4]
계산
[편집]수치와 변화
[편집]낮은(좁은) 맥압
[편집]높은(넓은) 맥압
[편집]지속적으로 높음
[편집]운동부터
[편집]임상적 중요성
[편집]심혈관 질환 및 맥압
[편집]약물이 맥압에 미치는 영향
[편집]맥압과 패혈증
[편집]같이 보기
[편집]각주
[편집]- ↑ 대한의협 의학용어 사전 https://www.kmle.co.kr/search.php?Search=pulse+pressure
- ↑ 가 나 다 Homan TD, Bordes SJ, Cichowski E (2022년 7월 12일). 〈Physiology, Pulse Pressure〉. 《StatPearls [Internet].》. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. PMID 29494015. 2019년 7월 21일에 확인함 – NCBI Bookshelf 경유.
- ↑ 가 나 Liaw SY, Scherpbier A, Klainin-Yobas P, Rethans JJ (September 2011). “A review of educational strategies to improve nurses' roles in recognizing and responding to deteriorating patients”. 《International Nursing Review》 58 (3): 296–303. doi:10.1111/j.1466-7657.2011.00915.x. PMID 21848774.
- ↑ 가 나 “Pulse pressure”. Cleveland Clinic. 2021년 7월 28일. 2023년 2월 10일에 확인함.
If you check your blood pressure regularly and notice you have an unusually wide (60 mmHg or more) or narrow pulse pressure (where your pulse pressure is less than one-quarter of the top blood pressure number), you should schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to talk about it. [...] Pulse pressures of 50 mmHg or more can increase your risk of heart disease, heart rhythm disorders, stroke and more. Higher pulse pressures are also thought to play a role in eye and kidney damage from diseases like diabetes.