Greater Orlando
Greater Orlando | |
|---|---|
| Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area | |
From top (left to right): Downtown Orlando skyline at night, Cinderella Castle at the center of Magic Kingdom in Walt Disney World, Orlando International Premium Outlets, Disney Springs at Walt Disney World, main entrance to Universal Studios Florida, and the campus of Rollins College in the community of Winter Park | |
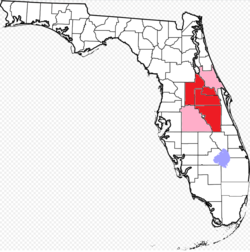 Greater Orlando with counties with lots of suburbs (in dark red) and counties with few suburbs (in light red) | |
| Coordinates: 28°32′N 81°23′W / 28.54°N 81.38°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State(s) | Florida |
| Largest city | Orlando |
| Other cities | Kissimmee Sanford Saint Cloud Winter Garden Daytona Beach Winter Park Windermere Apopka Ocoee Casselberry Oviedo Clermont Winter Springs Altamonte Springs Lake Mary Leesburg Bay Lake Lake Buena Vista |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4,011 sq mi (10,390 km2) |
| Highest elevation | Sugarloaf Mountain 312 ft (95 m) |
| Lowest elevation | Sea level 0 ft (0 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 2,673,376[1] |
| • Rank | 22nd in the U.S. |
| Gross Metropolitan Product | |
| • Total | US$167.279 billion (2021) |
The Orlando metropolitan area, also known as Central Florida, Greater Orlando, Metro Orlando, as well as for U.S. Census purposes as the Orlando–Kissimmee–Sanford, Florida Metropolitan Statistical Area, is a metropolitan area in the central region of the U.S. state of Florida. Its principal cities are Orlando, Kissimmee and Sanford. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget defines it as consisting of the counties of Lake, Orange (including Orlando), Osceola, and Seminole.[3]
References
[change | change source]- ↑ "Orlando-Kissimmee-Sanford, FL Metro Area Demographics and Housing 2020 Decennial Census".
- ↑ "GDP by county in 2021" (PDF). www.bea.gov.
- ↑ "Revised Delineations of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, Micropolitan Statistical Areas, and Guidance on the Uses of the Delineations of These Areas" (PDF). Executive Office of the President. July 21, 2023. p. 66. Retrieved July 21, 2023.
28°32′24″N 81°22′48″W / 28.54000°N 81.38000°W