女性尿道外括约肌
| 女性尿道外括约肌 | |
|---|---|
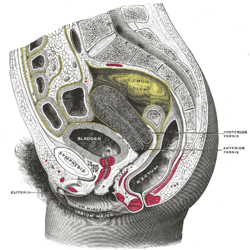 女性躯干下部右半部分矢状剖面图(括约肌没有标注) | |
 女性会阴部的肌肉(尿道括约肌没有标注) | |
| 基本信息 | |
| 神经 | 躯体神经纤维,从S2-S4经由阴部神经 |
| 相關動作 | 收缩尿道和阴道,控制排尿 |
| 标识字符 | |
| 拉丁文 | musculus sphincter urethrae externus urethrae femininae |
| TA98 | A09.2.03.006F |
| TA2 | 2422 |
| FMA | FMA:19778 |
| 格雷氏 | p.431 |
| 《肌肉解剖学术语》 [在维基数据上编辑] | |
女性尿道外括约肌(英語:External sphincter muscle of female urethra),是控制女性排尿的肌肉。肌肉纤维出现在耻骨下缘的两侧。它们穿过尿道前的耻骨弓,并绕过它与尿道和阴道之间对侧的肌肉纤维混合。
术语“尿道阴道括约肌”(urethrovaginal sphincter、sphincter urethrovaginalis)有时用于描述与阴道相邻的部分。[1][2][3][4][5]
“尿道收缩肌”(compressor urethrae)也被一些来源认为是单独的相邻肌肉。[6][7][8][9]
功能
[编辑]肌肉与受自主神经系统控制的尿道内括约肌一起帮助保持尿液的控制。外括约肌可防止尿液渗漏,因为肌肉通过起源于Onuf核的体细胞纤维强直收缩,并通过骶脊神经S2-S4,然后通过阴部神经到达肌肉上的突触。[7][10]
排尿开始于尿道外括约肌的自主松弛。这是通过在脑桥排尿中心产生并穿过下行网状脊髓束的信号抑制Onuf核中的体细胞神经元促进的。
参考文献
[编辑]本條目包含來自屬於公共領域版本的《格雷氏解剖學》之內容,而其中有些資訊可能已經過時。
- ^ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung. Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2005: 262. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
- ^ Rahn DD, Marinis SI, Schaffer JI, Corton MM. Anatomical path of the tension-free vaginal tape: reassessing current teachings. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195 (6): 1809–13. PMID 17132484. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2006.07.009.
- ^ Umek WH, Kearney R, Morgan DM, Ashton-Miller JA, DeLancey JO. The axial location of structural regions in the urethra: a magnetic resonance study in nulliparous women. Obstet Gynecol. 2003, 102 (5 Pt 1): 1039–45. PMC 1226706
 . PMID 14672484. doi:10.1016/j.obstetgynecol.2003.04.001.
. PMID 14672484. doi:10.1016/j.obstetgynecol.2003.04.001.
- ^ TA: A09.5.03.006F (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ FMA:30439 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Adam Mitchell; Drake, Richard; Gray, Henry David; Wayne Vogl. Gray's anatomy for students. Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. 2005: 396. ISBN 0-443-06612-4.
- ^ 7.0 7.1 Jung J, Ahn HK, and Huh Y. Clinical and Functional Anatomy of the Urethral Sphincter. Int Neurourol J. September 2012, 16 (3): 102–106. PMC 3469827
 . PMID 23094214. doi:10.5213/inj.2012.16.3.102.
. PMID 23094214. doi:10.5213/inj.2012.16.3.102.
- ^ TA : A09.5.03.005F (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ FMA : 30438 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)
- ^ Shah AP, Mevcha A, Wilby D, Alatsatianos A, Hardman JC, Jacques S, Wilton JC. Continence and micturition: An anatomical basis (PDF). Clin. Anat. November 2014, 27 (8): 1275–1283 [2023-01-31]. PMID 24615792. S2CID 21875132. doi:10.1002/ca.22388. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2019-12-15).