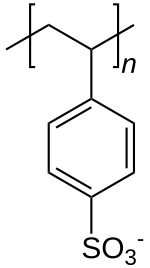
聚苯乙烯磺酸
 | |
| 臨床資料 | |
|---|---|
| 商品名 | 钠盐:Kayexalate, Kionex, Resonium A 钙盐:Calcium Resonium, Sorbisterit, Resikali 钾钠盐:Tolevamer |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682108 |
| 给药途径 | 口服, 保留 [灌肠] |
| ATC碼 | |
| 法律規範狀態 | |
| 法律規範 |
|
| 藥物動力學數據 | |
| 生物利用度 | None |
| 药物代谢 | None |
| 排泄途徑 | Faeces (100%) |
| 识别信息 | |
| |
| CAS号 | 9002-23-7 |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| 化学信息 | |
| 化学式 | [C8H7SO3−] n |
聚苯乙烯磺酸盐是一组用于治疗高鉀血症的药物。[1]效果通常需要数小时至数天。 [1]它们还用于在技术应用中从溶液中去除钾、钙和钠。
常见的副作用包括食欲不振、肠胃不适、便秘和低鈣血症。 [1]这些聚合物是衍生自聚苯乙烯,添加磺酸盐官能团。
聚苯乙烯磺酸钠于1958年在美国被批准用于医疗用途。[1]
聚苯乙烯磺酸盐于2000年代被开发出来,用于治疗艰难梭菌相关的腹泻,其名称为Tolevamer[2] ,但从未上市。
医疗用途
[编辑]
聚苯乙烯磺酸盐通常以钠或钙的形式提供。它可用作高钾血症(异常高血清钾水平)患者急性和慢性肾脏疾病的钾结合剂。 [3]然而,尚不清楚它是否有益,并且人们担心它与山梨醇结合使用时可能会产生副作用。 [4]
副作用
[编辑]肠道紊乱很常见,包括食欲不振、恶心、呕吐和便秘。在极少数情况下,它与结肠坏死有关。 [6]可能会出现低镁血症、低鈣血症和低鉀血症等电解质血液水平的变化。 [7]聚苯乙烯磺酸盐不应用于患有阻塞性肠病的人和肠道蠕动减弱的新生儿。[8]
肠道损伤
[编辑]截至2013年,共有58例因聚苯乙烯磺酸盐导致肠道损伤(包括结肠壞死)的报道[9]当与山梨醇联合使用时,已经报道了更多的病例,而单独使用时也发生了其他病例。 [9]
药物相互作用
[编辑]聚苯乙烯磺酸盐可以与消化道内的各种药物结合,从而降低其吸收和有效性。常见的例子包括锂、甲状腺素和洋地黄。2017年9月,FDA 建议将聚苯乙烯磺酸盐的剂量与任何其他口服药物分开至少三个小时,以避免任何潜在的相互作用。[10]
作用机制
[编辑]高钾血症
[编辑]聚苯乙烯磺酸盐在胃中释放钠或钙离子以交换氢离子。当树脂到达大肠时,氢离子被交换为游离钾离子;然后树脂通过粪便排出。净效应是降低可吸收到血液中的钾量并增加通过粪便排出的钾量。效果是降低体内钾含量,每1克树脂可交换1毫当量的钾。[8][11]
生产及化学结构
[编辑]聚苯乙烯磺酸,其盐为聚苯乙烯磺酸盐的酸,具有理想化式(CH2CHC6H4SO3H)n。该材料由聚苯乙烯磺化制备:
- (CH2CHC6H5)n + n SO3 → (CH2CHC6H4SO3H)n
这种转化有多种方法,可导致不同程度的磺化。通常聚苯乙烯是交联的,这可以防止聚合物溶解。由于磺酸基(SO3H)呈强酸性,因此该聚合物可以中和碱。通过这种方式,可以制备聚合物的各种盐,从而产生钠盐、钙盐和其他盐:
- (CH2CHC6H4SO3H)n + n NaOH → (CH2CHC6H4SO3Na)n + n H2O
这些含离子的聚合物称为离聚物。
替代磺化方法
[编辑]已知苯环会发生双取代,即使转化率远低于 100%。还发现了交联反应,其中两个磺酸基团缩合产生磺酰基交联。另一方面,使用较温和的条件如乙酰硫酸盐会导致磺化不完全。最近,报道了受保护的苯乙烯磺酸盐的原子转移自由基聚合(ATRP), [12][13]产生了明确的线性聚合物以及更复杂的分子结构。 [14]
化学品用途
[编辑]聚苯乙烯磺酸盐因其离子交换特性而有用。[15]线性离子聚合物通常是水溶性的,而交联材料(称为树脂)不溶于水。这些聚合物分为聚盐和离聚物。[15]
软化水
[编辑]水软化是通过将硬水渗透过交联聚苯乙烯磺酸钠形式的床来实现的。钙(Ca2+)和镁(Mg2+)等硬离子粘附在磺酸盐基团上,取代钠离子。所得钠离子溶液被软化。

其他用途
[编辑]聚苯乙烯磺酸钠用作水泥中的超塑化剂、棉花的染色改良剂以及燃料电池应用中的质子交换膜。在其酸形式下,该树脂在有机合成中用作固体酸催化剂。
参考
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Monograph for Professionals. Drugs.com. [25 October 2019]. (原始内容存档于2020-10-21) (英语).
- ^ Hinkson PL, Dinardo C, DeCiero D, Klinger JD, Barker RH. Tolevamer, an anionic polymer, neutralizes toxins produced by the BI/027 strains of Clostridium difficile. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. June 2008, 52 (6): 2190–2195. PMC 2415796
 . PMID 18391047. doi:10.1128/AAC.00041-08.
. PMID 18391047. doi:10.1128/AAC.00041-08.
- ^ MedlinePlus百科全书 High potassium level
- ^ Sterns RH, Rojas M, Bernstein P, Chennupati S. Ion-exchange resins for the treatment of hyperkalemia: are they safe and effective?. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. May 2010, 21 (5): 733–735. PMID 20167700. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010010079
 .
.
- ^ Polystyrene sulfonate. Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference. Medicines Complete. [27 November 2009]. (原始内容存档于2021-08-28).
- ^ Rogers FB, Li SC. Acute colonic necrosis associated with sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) enemas in a critically ill patient: case report and review of the literature. The Journal of Trauma. August 2001, 51 (2): 395–397. PMID 11493807. doi:10.1097/00005373-200108000-00031.
- ^ KAYEXALATE (sodium polystyrene sulfonate). FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Revised 07/2017 (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) Retrieved 2018-10-21
- ^ 8.0 8.1 FDA专业药物信息 for Kayexalate.
- ^ 9.0 9.1 Harel Z, Harel S, Shah PS, Wald R, Perl J, Bell CM. Gastrointestinal adverse events with sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) use: a systematic review. The American Journal of Medicine. March 2013, 126 (3): 264.e9–264.24. PMID 23321430. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.08.016.
- ^ Office of the Commissioner. Safety Alerts for Human Medical Products - Kayexalate (sodium polystyrene sulfonate): Drug Safety Communication - FDA Recommends Separating Dosing. www.fda.gov. [2017-09-19] (英语).
- ^ Chaitman M, Dixit D, Bridgeman MB. Potassium-Binding Agents for the Clinical Management of Hyperkalemia. P & T. January 2016, 41 (1): 43–50. PMC 4699486
 . PMID 26765867.
. PMID 26765867.
- ^ Sikkema FD, Comellas-Aragonès M, Fokkink RG, Verduin BJ, Cornelissen JJ, Nolte RJ. Monodisperse polymer-virus hybrid nanoparticles. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry. January 2007, 5 (1): 54–57. PMID 17164905. doi:10.1039/b613890j.
- ^ Lienkamp K, Schnell I, Groehn F, Wegner G. Polymerization of Styrene Sulfonate Ethyl Ester by ATRP: Synthesis and Characterization of Macromonomers for Suzuki Polycondensation. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics. 2006, 207 (22): 2066–2073. doi:10.1002/macp.200600322.
- ^ Lienkamp K, Ruthard C, Lieser G, Berger R, Groehn F, Wegner G. Polymerization of Styrene Sulfonate Ethyl Ester and Styrene Sulfonate Dodecyl Ester by ATRP: Synthesis and Characterization of Polymer Brushes. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics. 2006, 207 (22): 2050–2065. S2CID 98278283. doi:10.1002/macp.200600321.
- ^ 15.0 15.1 De Dardel F, Arden TV. Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. 2008. ISBN 978-3527306732. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_393.pub2.