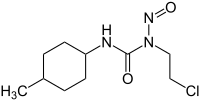
Sémustine
| Sémustine | |||
| |||
| Identification | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Nom UICPA | (chloro-2 éthyl)-1 (méthyl-4 cyclohexyl)-3 nitroso-urée | ||
| Synonymes |
méthyllomustine, méthyl-CCNU |
||
| No CAS | |||
| No ECHA | 100.162.271 | ||
| No RTECS | YS5000000 | ||
| Code ATC | L01 | ||
| PubChem | 5198 | ||
| SMILES | |||
| InChI | |||
| Propriétés chimiques | |||
| Formule | C10H18ClN3O2 [Isomères] |
||
| Masse molaire[1] | 247,722 ± 0,012 g/mol C 48,48 %, H 7,32 %, Cl 14,31 %, N 16,96 %, O 12,92 %, |
||
| Précautions | |||
| SGH[2] | |||
| H300, H311, H315, H319, H331, H335, H350, H360, P201, P261, P264, P280, P301+P310 et P305+P351+P338 |
|||
| Transport[2] | |||
|
|||
| Écotoxicologie | |||
| DL50 | 49,9 mg/kg (souris, oral)[3] | ||
| LogP | (octanol/eau) 3,3[3] | ||
| Considérations thérapeutiques | |||
| Classe thérapeutique | agent chimiothérapeutique | ||
| Unités du SI et CNTP, sauf indication contraire. | |||
| modifier |
|||
La sémustine est un composé organique de la famille des nitrosourées, anciennement utilisé en chimiothérapie[4]. Elle est structurellement similaire à la lomustine, la différence étant le groupe méthyle supplémentaire sur le cyclohexane.
Il a été retiré du marché du fait de ses effets cancérigènes, le CIRC l'ayant classé dans les cancérogènes du groupe 1[5].
Sécurité
[modifier | modifier le code]Le TDLo pour les êtres humains adultes se situe entre 6 et 90 mg/kg (oral), celui des enfants vaut 37 950 mg/kg/2 ans (oral)[3].
- 5 550 mg/kg/30 semaines (enfant, oral)
- 25 mg/kg (chien, oral)
- 14 mg/kg (chien, i.v.)
- 100 mg/kg (singe, oral)
- 45 mg/kg (singe, i.v.)
- 100 mg/kg (rat, s.c.)
Notes et références
[modifier | modifier le code]- ↑ Masse molaire calculée d’après « Atomic weights of the elements 2007 », sur www.chem.qmul.ac.uk.
- Fiche Sigma-Aldrich du composé Semustine, consultée le 23/04/2011.
- (en) « Sémustine », sur ChemIDplus.
- ↑ « Radiation therapy and fluorouracil with or without semustine for the treatment of patients with surgical adjuvant adenocarcinoma of the rectum. Gastrointestinal Tumor Study Group », Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 10, no 4, , p. 549–557 (PMID 1548520)
- ↑ http://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancercauses/othercarcinogens/generalinformationaboutcarcinogens/known-and-probable-human-carcinogens, Known and Probable Human Carcinogens, American Cancer Society


