Lingua chipewyan
| Chipewyan ᑌᓀ ᓱᒼᕄᓀ ᔭᕠᐁ Dënë Sųłinë́ Yatıé | ||
|---|---|---|
| Falado en: | Canadá | |
| Rexións: | Norte de Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba; sur de Territorios do Noroeste e Nunavut | |
| Total de falantes: | 11.895[1] | |
| Familia: | Linguas atapascanas | |
| Status oficial | ||
| Lingua oficial de: | Territorios do Noroeste[2] | |
| Códigos de lingua | ||
| ISO 639-1: | --
| |
| ISO 639-2: | chp | |
| ISO 639-3: | chp
| |
| SIL: | CPW
| |
| Mapa | ||

| ||
| Status | ||
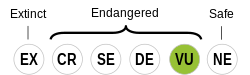 | ||
A lingua chipewyan (tamén nomeada Dënë Sųłinë́ Yatıé), é o idioma falado polo pobo chipewyan, tribo da parte central do Canadá. Forma parte da familia atapascana e está relacionada con linguas como o navaho. O chipewyan ten uns 12.000 parlantes canadenses, maioritariamente en Saskatchewan, Alberta e Territorios do Noroeste,[1] mais só ten a condición de oficialidade nos Territorios do Noroeste, canda outras oito linguas indíxenas de América: cree, dogrib, gwich'in, inuktitut, inuinnaqtun, inuvialuktun, slave norte e slave sur.[4]
Sons
[editar | editar a fonte]Consoantes
[editar | editar a fonte]O chipewyan posúe 39 consoantes:
| Bilabial | Interdental | Dental | Postalveolar | Velar/Uvular | Glotal | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| central | lateral | xorda | labial | ||||||
| Nasal | m | n | |||||||
| Oclusiva | xorda | p | t | k | kʷ | ||||
| aspirada | tʰ | kʰ | kʷʰ | ||||||
| exectiva | tʼ | kʼ | kʼʷ | ʔ | |||||
| Africada | xorda | tθ | ts | tɬ | tʃ | ||||
| aspirada | tθʰ | tsʰ | tɬʰ | tʃʰ | |||||
| exectiva | tθʼ | tsʼ | tɬʼ | tʃʼ | |||||
| Fricativa | xorda | θ | s | ɬ | ʃ | χ | χʷ | h | |
| sonora | ð | z | ɮ | ʒ | ʁ | ʁʷ | |||
| Vibrante | r | ||||||||
A velar fricativa é actualmente uvular.
Vogais
[editar | editar a fonte]O chipewyan ten 6 vogais distintas:
| Anterior | Central | Posterior | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fechada | i | u | |
| Semifechada | e | o | |
| Semiaberta | ɛ | ||
| Aberta | a |
A maior parte das vogais poden dividirse en:
- oral ou nasal
- curta ou longa
Como consecuencia, o chipewyan emprega 18 fonemas vocálicos:
| Anterior | Central | Posterior | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| curta | longo | curta | longa | curta | longa | ||
| Fechada | oral | i | iː | u | uː | ||
| nasal | ĩ | ĩː | ũ | ũː | |||
| Semifechada | e | o | |||||
| Semiaberta | oral | ɛ | ɛː | ||||
| nasal | ɛ̃ | ɛ̃ː | |||||
| Aberta | oral | a | aː | ||||
| nasal | ã | ãː | |||||
O chipewyan tamén ten 9 ditongos orais e nasais da forma vogal + /j/.
| Anterior | Central | Posterior | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| oral | nasal | oral | nasal | oral | nasal | |
| Fechada | uj | ũj | ||||
| Media | ej | ẽj | əj | oj | õj | |
| Aberta | aj | ãj | ||||
Notas
[editar | editar a fonte]- ↑ 1,0 1,1 "Statistics Canada: 2006 Censo". Arquivado dende o orixinal o 16 de outubro de 2013. Consultado o 14 de xullo de 2008.
- ↑ "Official Languages of the Northwest Territories" (PDF) (en inglés). Northwest Territories – Education, Culture and Employment. Arquivado dende o orixinal (PDF) o 2013-12-06. Consultado o 2015-10-18. (map)
- ↑ Moseley, Christopher e Nicolas, Alexandre. "Atlas of the world's languages in danger". unesdoc.unesco.org. Consultado o 11 de xullo de 2022.
- ↑ Lei de Idiomas Oficiais dos Territorios do Noroeste de 1988 (con emendas en 1988, 1991-1992, 2003)
Véxase tamén
[editar | editar a fonte]| Vexa a proba da Wikipedia en Lingua chipewyan |
| A Galipedia ten un portal sobre: Pobos indíxenas de América |
Ligazóns externas
[editar | editar a fonte]- Chipewyan en Ethnologue(en inglés)
- Our Languages: Dene (Saskatchewan Indian Cultural Centre)(en inglés)
- Historia e antecedentes(en inglés)
- Reservas(en inglés)
- mapas Reservas(en inglés)
- Preservación/Revitalización(en inglés)
- Alfabeto(en inglés)
- Gramática(en inglés)
- Palabras (inclúe ficheiros de son)(en inglés)
Bibliografía
[editar | editar a fonte]- Cook, Eung-Do. (2004). A grammar of Dëne Sųłiné (Chipewyan). Algonquian and Iroquoian Linguistics - Special Athabaskan Number, Memoir 17. Winnipeg: Algonquian and Iroquoian Linguistics. ISBN 0-921064-17-9.
- Cook, Eung-Do. 2006. "The Patterns of Consonantal Acquisition and Change in Chipewyan (Dene Suline)". International Journal of American Linguistics. 72, no. 2: 236.
- De Reuse, Willem. 2006. "A Grammar of Dene Suline (Chipewyan) (Cook)". International Journal of American Linguistics. 72, no. 4: 535.
- Elford, Leon W. Dene sųłiné yati ditł'ísé = Dene sųłiné reader. Prince Albert, SK: Northern Canada Mission Distributors, 2001. ISBN 1-896968-28-7
- Gessner, S. 2005. "Properties of Tone in Dene Suline". Amsterdam Studies in the Theory and History of Linguistic Science. Series IV, Current Issues in Linguistic Theory. 269: 229-248.
- Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (Ed.). (2005). Ethnologue: Languages of the world (15th ed.). Dallas, TX: SIL International. ISBN 1-55671-159-X. (Versión online: http://www.ethnologue.com).
- Li, Fang-Kuei. (1946). Chipewyan. In C. Osgood & H. Hoijer (Eds.), Linguistic structures of native America (pp. 398–423). Nova York: The Viking Fund.
- Osgood, Cornelius; & Hoijer, Harry (Eds.). (1946). Linguistic structures of native America. Viking fund publications in anthropology (No. 6). Nova York: The Viking Fund. (Reprinted 1963, 1965, 1967, & 1971, Nova York: Johnson Reprint Corp.).
