Sông Atbarah
| Sông Atbarah | |
|---|---|
 Upper Atbara and Setit Dam Complex Hydroelectric Power Plant | |
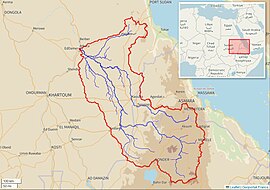 Atbarah River Basin (Interactive map) | |
| Vị trí | |
| Countries | |
| Đặc điểm địa lý | |
• vị trí | Discharges into the Nile |
• tọa độ | 17°40′41″B 33°58′25″Đ / 17,6781°B 33,9735°Đ |
| Độ dài | 805 kilômét (500 mi) |
| Diện tích lưu vực | 69.000 kilômét vuông (27.000 dặm vuông Anh) |
| Lưu lượng | |
| • trung bình | 374 m3/s (13.200 cu ft/s) |
Sông Atbarah (tiếng Ả Rập: نهر عطبرة; transliterated: Nahr 'Atbarah), còn được biết đến với tên Sông Nile Đỏ hay Sông Nile Đen, là một con sông ở phía đông bắc châu Phi. Nó khởi nguồn từ phía tây bắc Ethiopia, cách Hồ Tana khoảng 50 km về phía bắc và cách Gondar 30 km về phía tây . Sau đó sông trải dài khoảng 805 km (500 mi) trước khi đến hợp lưu sông Nile ở vùng trung bắc Sudan, tại vị trí đô thị Atbarah (17°40′37″B 33°58′12″Đ / 17,677°B 33,97°Đ). Các phụ lưu bao gồm sông Tekezé, có lẽ là phần khởi nguồn của Atbarah, vì sôngTekezé chảy một đoạn dài trước khi hợp lưu hai con sông tại (at 14° 10' N, 36° E) đông bắc Sudan. Sông Atbarah là phụ lưu cuối của sông Nile trước khi sông đổ ra Địa trung hải.
Trong phần lớn thời gian hằng năm, lưu lượng dòng sông này chỉ lớn hơn một dòng suối nhỏ. Tuy nhiên trong mùa mưa (từ tháng 7 đến tháng 10), mực nước sông Atbarah có khi dâng cao đến 18 ft (5 m) so với mực nước thông thường. Tại thời điểm này, con sông trở thành hàng rào tự nhiên ngăn cách phía bắc và nam của Amhara (vùng) thuộc Ethiopia. Ngoài Tekezé, các phụ lưu quan trọng khác của Atbarah bao gồm Shinfa River bắt nguồn từ phía tây Hồ Tana, và Greater Angereb khởi nguồn từ phía bắct thành phố Gondar.
Lịch sử
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Ghi nhận sớm nhất về sông Atbarah là bởi Strabo (16.4.8), khi đó ông ghi chép con sông với tên Astaboras (tiếng Hy Lạp: Ασταβόρας).[1] Các tác giả cổ đại khác đề cập đến cái tên này bao gồm Agatharchides, ông ghi nhận nó dưới tên Astabaras (tiếng Hy Lạp: Ασταβάρας),[1] và Ptolemy (Geography 4.7).[2] Richard Pankhurst và các tác giả khác tranh luận rằng tên này nên được hiểu là "River of the Boras people", where asta can be related to Proto-Nubian asti "water",[1] while -boras can be linked to a number of Roman allusions to a tribe named the Bora (Bera), who lived near Meroe,[3] and another tribe named the Megabares (tiếng Hy Lạp: Μεγάβαροι in Eratosthenes and Strabo, tiếng Latinh: Megabarri in Pliny the Elder).[1] Pliny the Elder provides a slightly different etymology of Astaboras, stating that "in the language of the local people" the name means "water coming from the shades below" (N.H. 5.10).
Tháng 4 năm 1898 một trận đánh quan trọng đã diễn ra cạnh con sông trong Anglo-Egyptian invasion of Sudan 1896–1899 between Mahdist forces and an Anglo-Egyptian Army under the command of Lord Kitchener, which resulted in the destruction of the 20,000-strong Mahdist detachment.[4]
Năm 1964, the river was dammed by the Khashm el-Girba Dam near Kassala in Sudan to provide irrigation to the newly built town of Halfa Dughaym in an otherwise fairly arid region and to resettle the Sudanese population driven away by the Aswan High Dam (Sad al-Aali) in Egypt, which flooded 500 km of the Nile Valley in southern Egypt and northern Sudan.[5]
Construction on a $1.9 billion twin dam project about 20 km upstream from the confluence of the Upper Atbara and Setit rivers, the Rumela and Burdana dams, began in 2011 and was inaugurated by President Omar al-Bashir in February 2017.[6]
Hydrology
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Average monthly flow (1912–1982) of the Atbarah measured approximately 25 km upstream of its mouth, measured in m3/s:[7]

Xem thêm
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Tham khảo
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]- ^ a b c d Claude Rilly, Le méroïtique et sa famille linguistique, Peeters, Louvain 2010, p. 179
- ^ “LacusCurtius • Ptolemy's Geography — Book IV, Chapter 7”. Penelope.uchicago.edu. Truy cập ngày 10 tháng 12 năm 2013.
- ^ Richard Pankhurst, The Ethiopian Borderlands (Lawrenceville: Red Sea Press, 1997), p. 27
- ^ Winston Churchill (1899). The River War Volume 1. Longmans. tr. 416 Chapter XIII.
- ^ Hurni, Hans; Tato, Kebede; Zeleke, Gete (tháng 5 năm 2005). “The Implications of Changes in Population, Land Use, and Land Management for Surface Runoff in the Upper Nile Basin Area of Ethiopia”. Mountain Research and Development. 25 (2): 147–154. doi:10.1659/0276-4741(2005)025[0147:tiocip]2.0.co;2. ISSN 0276-4741.
- ^ Gregory B. Poindexter (2 tháng 2 năm 2017). “Sudan inaugurates US$1.9 billion Upper Atbara and Setit Dam hydropower project”. HydroWorld. Truy cập ngày 4 tháng 11 năm 2018.
- ^ “Nile - Kilo 3”. University of New Hampshire. 26 tháng 2 năm 2000.
Liên kết ngoài
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]- Maps of Ethiopia - Perry–Castañeda Library Map Collection, University of Texas
![[Review sách] Tàn ngày để lại: Còn lại gì sau một quá khứ huy hoàng đã mất](https://down-tx-vn.img.susercontent.com/sg-11134201-7rdx5-lxqgdohyz3nse3.webp) GIẢM
27%
GIẢM
27%
 GIẢM
12%
GIẢM
12%
![[Review Sách] Đọc vị tâm trí](https://down-bs-vn.img.susercontent.com/sg-11134201-7qvdk-libws1cgh4ks57.webp) GIẢM
3%
GIẢM
3%
 GIẢM
17%
GIẢM
17%
 GIẢM
32%
GIẢM
32%
 GIẢM
25%
GIẢM
25%



