Hàm tri

Hàm tri hay còn gọi là hàm tam giác là một hàm số toán học được định nghĩa như sau:
Hoặc tương đương với tích chập của 2 hàm rect đơn vị giống nhau:
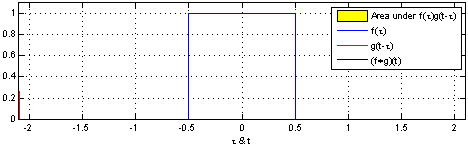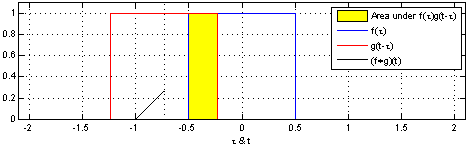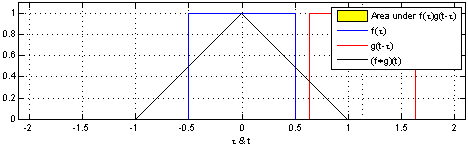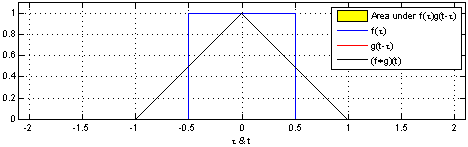
Hàm tri cũng có thể được biểu diễn bởi hàm rect và hàm trị tuyệt đối:
Hàm số này được sử dụng nhiều trong xử lý tín hiệu và kỹ thuật truyền thông.
Mở rộng
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Với các giá trị :
Biến đổi Fourier
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]Biển đổi Fourier dễ dàng bằng cách sử dụng công thức tích chập của 2 hàm rect:
với si là hàm sinc không chuẩn.
Tham khảo
[sửa | sửa mã nguồn]- Signalübertragung (ấn bản thứ 6.). Springer Verlag. 1995. ISBN 3-540-54824-6.
|first=thiếu|last=(trợ giúp)
Chúng tôi bán
![[Review Sách] Suy tưởng](https://down-bs-vn.img.susercontent.com/vn-11134207-7r98o-llnmys2twmz345.webp) GIẢM
3%
GIẢM
3%
174.000 ₫
179.000 ₫
 GIẢM
25%
GIẢM
25%
130.000 ₫
174.000 ₫
![[Review sách] Normal people - Sally Rooney](https://down-bs-vn.img.susercontent.com/sg-11134201-22090-edroebrkpwhvaf.webp) GIẢM
16%
GIẢM
16%
548.265 ₫
650.900 ₫
 GIẢM
16%
GIẢM
16%
169.000 ₫
202.000 ₫
![[Review Sách] 7 Định luật giảng dạy](https://down-bs-vn.img.susercontent.com/vn-11134207-7qukw-lidxs3ynamto6c.webp) GIẢM
12%
GIẢM
12%
218.000 ₫
248.000 ₫
 GIẢM
26%
GIẢM
26%
111.000 ₫
149.000 ₫









